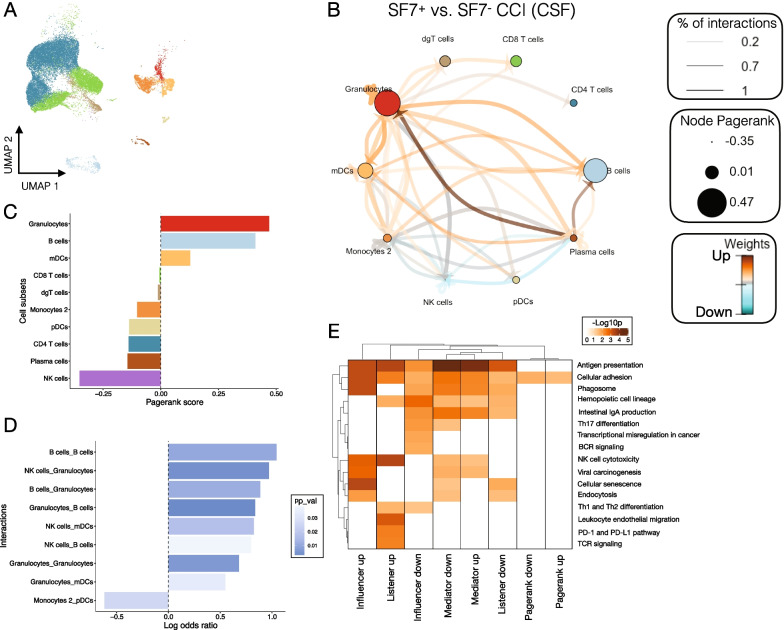
Fig. 7.
B cells function as central hub orchestrating cell–cell interactions between SLAMF7+ cells in the CNS. A UMAP of 31,063 immune cells from the CSF of six healthy controls and six MS patients reanalyzed from [28]. B Cell–cell interaction (CCI) network comparing differential cellular interaction networks between SLAMF7+ and SLAMF7− immune cells from A. Each node is a cell type which is scaled according to its PageRank score (centrality in SLAMF7+ vs. SLAMF7− networks). Arrows connecting nodes show directionality of cell–cell interactions, are sized based on the percent of interactions comparing SLAMF7+ to SLAMF7− networks, and are colored based on whether the interactions are up- or down-regulated in SLAMF7+ vs. SLAMF7− networks. C Bar plot of PageRank scores from the CCI network in B highlighting B cells and granulocytes as being the most important cell types in SLAMF7+ immune cell interaction networks compared to SLAMF7− networks. D Bar plot showing the log odds ratio for all significant cell–cell interactions between SLAMF7+ vs. SLAMF7− networks. A positive log odds ratio indicates that interaction is enriched in a network composed of SLAMF7+ immune cells compared to SLAMF7− immune cells. E Heatmap of differentially regulated KEGG pathways for the topological measures used to calculate the CCI network in B. Influencers are the outgoing signals from each cell type, listeners are the incoming signals to each cell type, moderators measure the importance of a cell type to mediate communication between cell types, and PageRank is the importance of each cell type to orchestrating cell–cell communications in a network [32]. dgT cells, δγ T cells