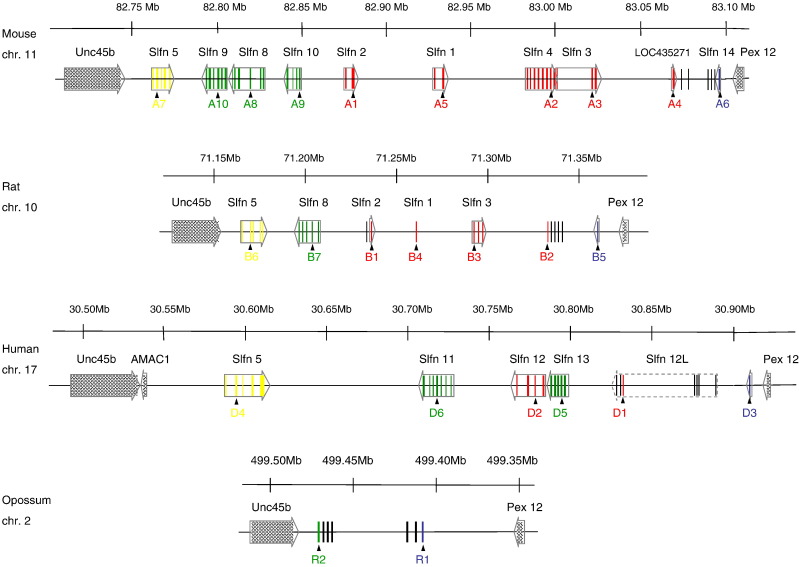
Fig. 2.
Orthologous regions in mouse, rat, human and opossum that contain the Slfn genes. Indicated are the Ensembl annotated Slfn genes and the related sequences found in our search, their exons, and direction of transcription when expression support was found (Appendix A). The location of the sequences identified and used in our phylogenetic analyses (Fig. 4, Fig. 5) is indicated below with arrows. Colors indicate their relationships according to our phylogenetic results (red = Group 1; yellow = Group 2; blue = Group 3; green = “Group 4”; black = unidentified). The position of the human Slfn12L predicted transcript is indicated, although the dashed arrow box also encompasses several additional sequences that are not included in the prediction but that we subsequently identified as Slfns (Appendix A). Opossum R2 sequence was not included in the phylogenetic analysis (see Methods), but our analyses indicate that it is more similar to Slfn8, 9 and 10 (Group 4) sequences than to any other mouse sequences (data not shown).