Fig. 1.
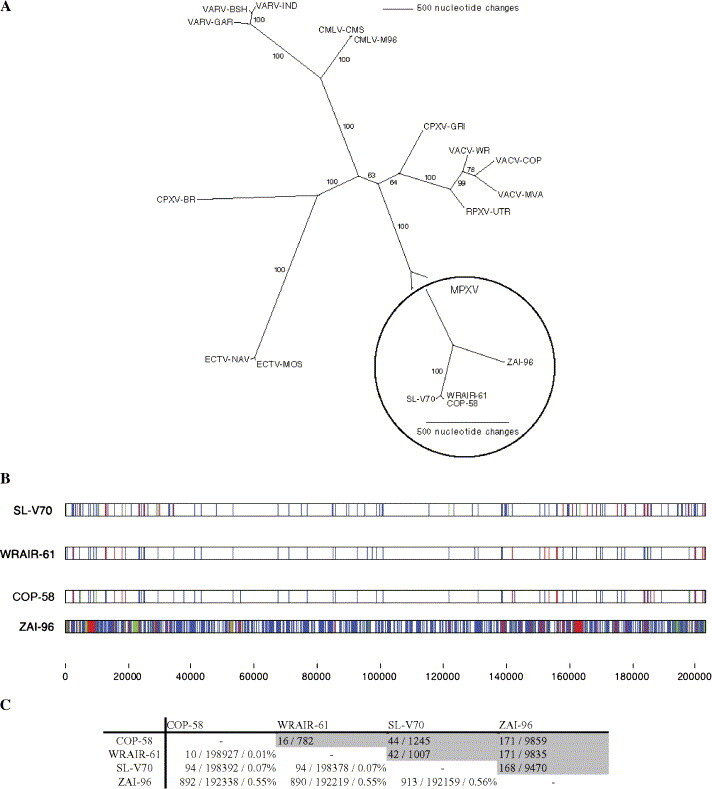
Genomic comparison of West African and Congo basin isolates of MPXV. (A) OPV phylogenetic predictions based upon the multiple nucleic acid sequence alignments of the core genomic region of each representative orthopoxvirus species, strain, or isolate. Bootstrap resampling confidence percentage based on 1000 replicates are displayed at each branch point. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of nucleotide changes. (B) CLUSTALW software was used to align the genomes of SL-V70, COP-58, WRAIR-61, and ZAI-96 and the alignment was manually optimized using Base-By-Base (Brodie et al., 2004). Each mismatched base was identified as a substitution (blue bar), deletion (red bar), or insertion (green bar) relative to a consensus; blue bars in all genomes indicate no consensus. InDels were counted as one mismatch regardless of size. The scale is such that several substitutions in close proximity may generate a single blue bar. (C) Summary of nucleotide difference comparisons: upper (grey) = gap number (segments) / total gap length; lower = number substitutions / number identical (non-gap) residues / percent difference (includes number of gaps).
