Figure 3. Genetic Evolution of Thyroid Cancers.
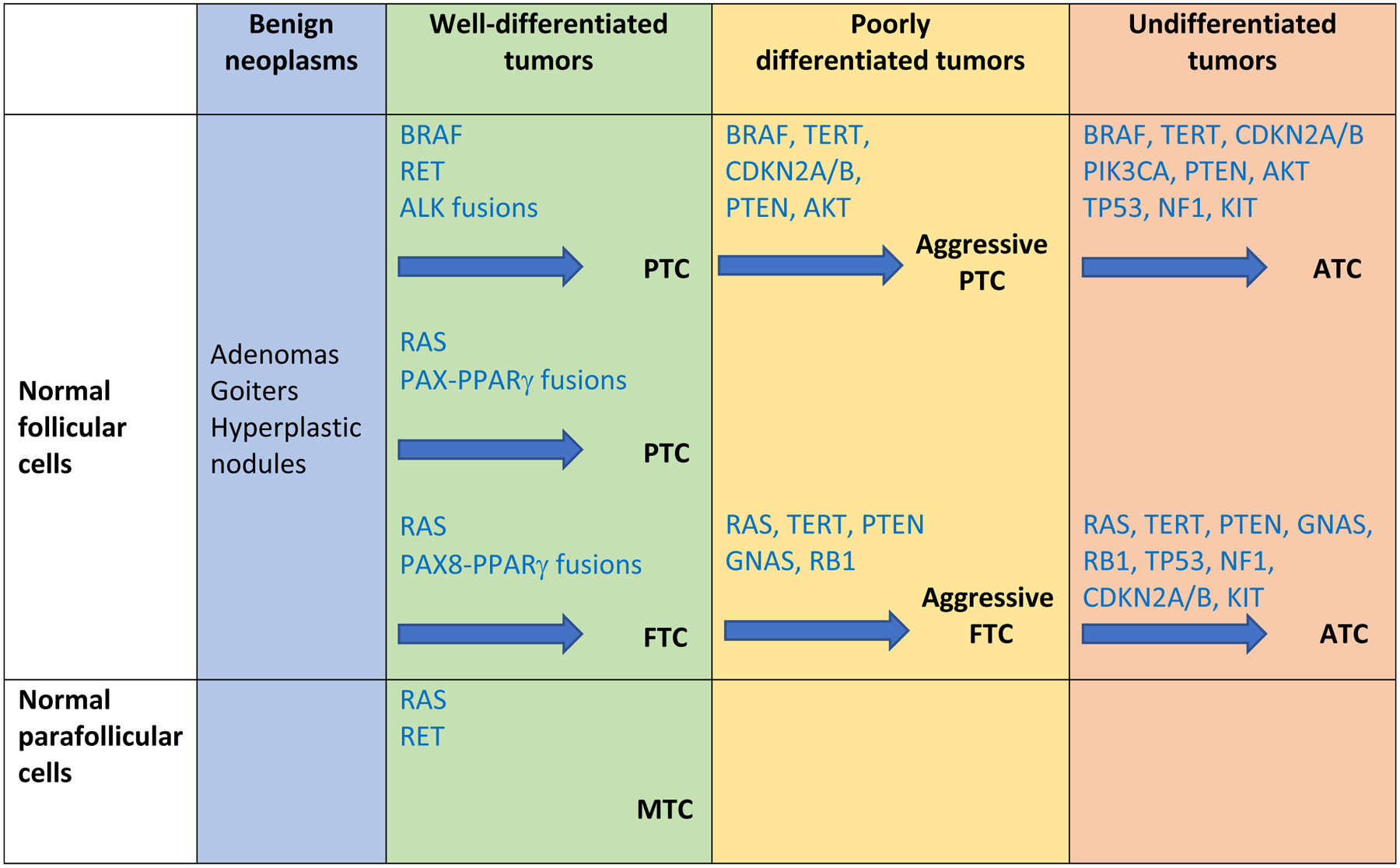
The diagram postulates that transformation from normal thyroid cells is associated with accumulation of an increasing number of mutated genes, starting with early driver mutations in the BRAF, RAS or RET genes. Tumors can then evolve to a less differentiated morphology and more aggressive behavior in poorly differentiated thyroid cancers (PDTC) with acquisition of TERT promoter and/or PTEN mutations. Ultimately the tumors can develop into ATC through acquisition of additional mutations in TP53, NF1 and PIK3CA. Adapted from Pozdeyev et al., 2018.
