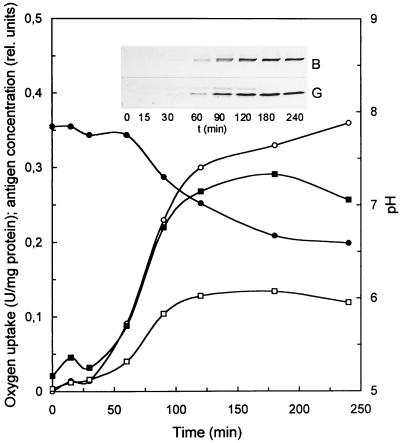
FIG. 3.
Thiosulfate-induced formation of SoxB and SoxG. P. pantotrophus was cultivated in mineral medium (400 ml) with 10 mM sodium succinate plus 10 mM glucose in a 1-liter baffled Erlenmeyer flask. After the cells reached the stationary phase at an optical density at 436 nm of 6.35, sodium thiosulfate (20 mM) was added. Cells (0.7 ml) were collected by centrifugation, resuspended with 150 μl of SDS sample buffer, and incubated at 60 and 100°C for 5 min each. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation, and the supernatant was diluted with four aliquots of sample buffer. From this preparation, 20 μg of protein was subjected to SDS-PAGE. Immunoblotting was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Signal intensity was quantified using the Scion Image software. ○, oxygen uptake rate; ●, pH; ▪, SoxG; □, SoxB.