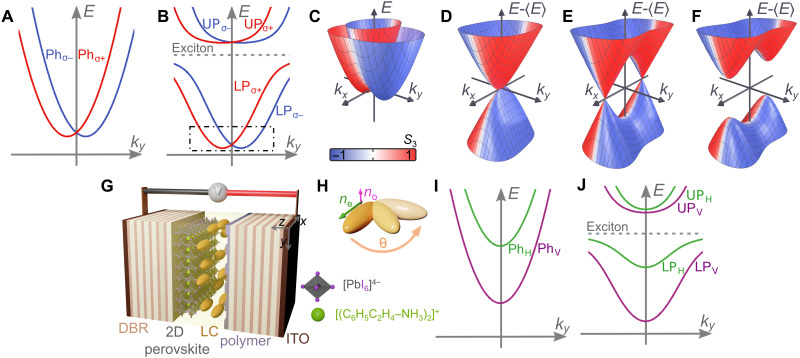
Fig. 1. LC microcavity with 2D perovskite.
Schematic dispersion relation of (A) bare cavity photon modes in the RD SOC regime and (B) in the strong light-matter coupling regime. (C) Dispersion relation for the bottom of the lower polariton branch [the region marked by a dot-dashed rectangle in (B)]. (D) Same as (C) with the dispersion subtracted by its mean value ⟨E⟩ to more clearly show the intersection points. Energy of the modes for (E) positive horizontal-vertical (H-V) splitting and (F) with broken inversion symmetry. (G) Schematic representation of the LC microcavity with the two-dimensional (2D) hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite layer and LC molecules oriented parallel to the x-y plane at zero voltage. (H) Rotation of an LC molecule under applied voltage with refractive indices (no, ne) and angle θ in the z-x plane. We also show the bare photon (I) and polariton (J) dispersions in the linear H-V polarization basis in the absence of voltage to highlight their splitting. ITO, indium tin oxide.