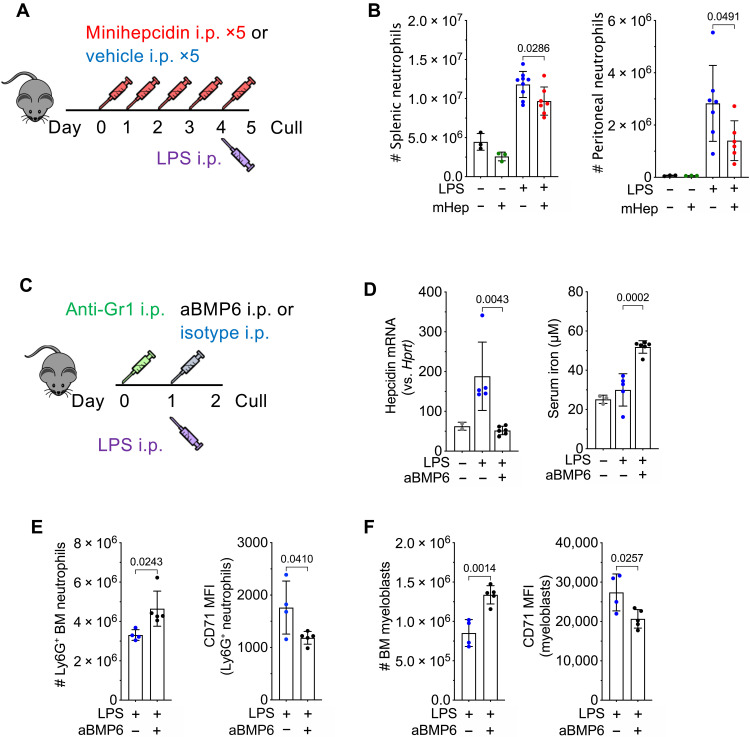
Fig. 4. Modulation of hepcidin during inflammation alters neutrophil production.
(A) Experimental scheme for investigation of effect of sustained hypoferremia on neutrophil response to sterile inflammatory challenge. (B) Number of mature Ly6G+ neutrophils in the spleen and peritoneal cavity in mice treated as in (A). t test. Means ± SD. (C) Experimental scheme for investigation of effect of endogenous hepcidin response on granulopoiesis. (D) Liver hepcidin expression (Mann-Whitney test) and serum iron from mice treated as in (C). Means ± SD. Non-LPS–treated control group was treated with aGr1 24 hours before culling to reflect the systemic iron environment before LPS injection. Representative of two independent experiments. (E) Number of BM Ly6G+ neutrophils and CD71 MFI on Ly6G+ neutrophils in mice treated as in (C). t test. Means ± SD. Representative of three independent experiments. (F) Number of BM c-kit+ CD115− Ly6G− myeloblasts and CD71 MFI on c-kit+ myeloblasts in mice treated as in (C). t test. Means ± SD. Representative of three independent experiments.