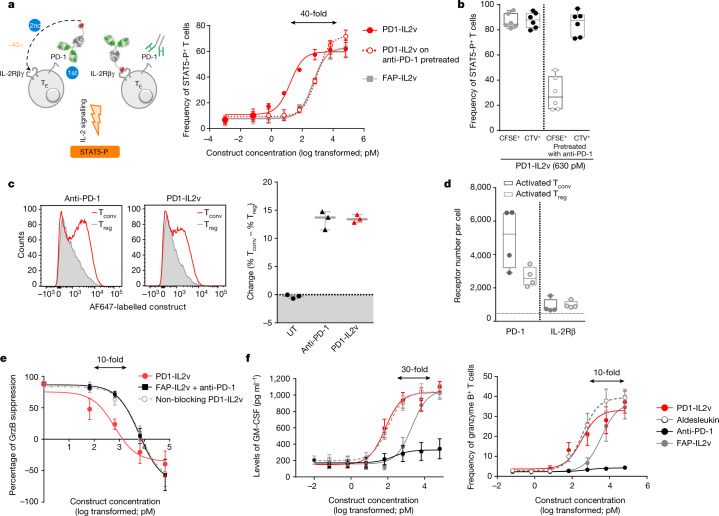
Fig. 1. PD1-IL2v mediates cis delivery of IL-2v to PD-1+ T cells, providing preferential stimulation of PD-1+ T cells, overcoming Treg-mediated suppression and inducing T cell effector functions.
a, Frequency of in vitro-activated polyclonal human STAT5-P+CD4+ T cells following exposure for 12 min to increasing concentrations of either PD1-IL2v or FAP-IL2v. As an additional control, a portion of the PD-1+ T cells were pretreated with anti-PD-1 antibody to prevent PD-1-mediated targeting of PD1-IL2v (dotted line) (n = 3 healthy donors, 3 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.). TE, effector T cell; αPD-1, anti-PD-1 antibody. Arrows indicate the difference in potency. b, Frequency of in vitro-activated polyclonal human STAT5-P+CD4+ T cells following exposure for 12 min to 630 pM PD1-IL2v of CFSE-labelled PD-1+ or PD-1-preblocked (PD-1–) T cells co-cultured with CTV-labelled PD-1+ T cells (n = 6 healthy donors, 3 independent experiments; box plots represent the median, minimum/maximum and individual points). c, Left, flow cytometry histogram plots of binding competition of directly conjugated anti-PD-1 antibody or PD1-IL2v to human CD4+ Tconv versus Treg cells, cultured together, from one representative donor of three. Right, change in the frequency of human CD4+ Tconv and Treg cells stained with labelled anti-PD-1 antibody or PD1-IL2v (n = 3 healthy donors, 3 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.). UT, untreated. d, Number of PD-1 receptors and IL-2Rβ per T cell on Tconv and Treg cells (n = 4 healthy donors; box plots represent the median, minimum/maximum and individual points). e, Treg suppression of Tconv secretion of granzyme B (GrzB) in the presence of increasing concentrations of PD1-IL2v, FAP-IL2v in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody, and non-blocking PD1-IL2v (n = 5 healthy donors, 5 independent experiments; mean ±s.e.m.). f, Dose-dependent GM-CSF and granzyme B secretion by in vitro-activated polyclonal human CD4+ T cells following stimulation for 5 d with increasing concentrations of PD1-IL2v, aldesleukin, FAP-IL2v or anti-PD-1 antibody (n = 4 healthy donors, 2 independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m.).