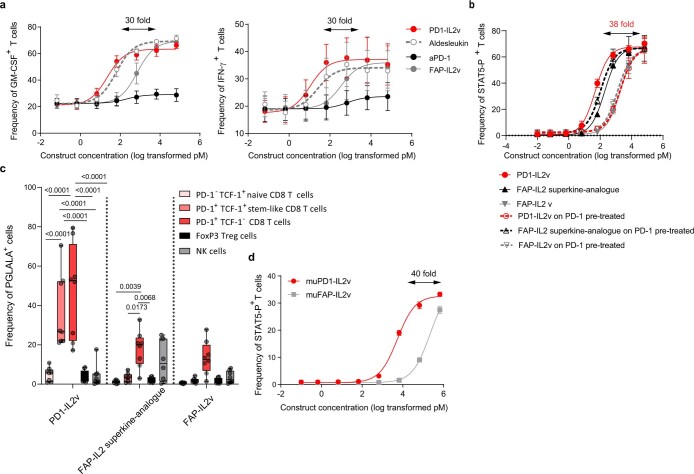
Extended Data Fig. 4. In vitro CD4 T cell activation and cytokine release by PD1-IL2v and in vivo expansion of antigen-specific polyfunctional CD8 T cells by muPD1-IL2v.
a. Dose dependent increase in frequencies of GM-CSF+ and IFN-γ+ human polyclonal CD4 T cells upon 5 days of in vitro stimulation with increasing concentrations of either PD1-IL2v, Aldesleukin, FAP-IL2v or PD-1 antibody (n = 4 healthy donors, 2 independent experiments, mean ± SEM). b. Frequency of in vitro activated, polyclonal human STAT5-P+ CD4 T cells upon exposure for 12 min to increasing concentrations of either PD1-IL2v, FAP-IL2v or FAP-IL2 superkine-analogue. As additional control, part of the PD-1+ T cells were pre-treated with PD-1 antibody to prevent PD-1-mediated targeting of PD1-IL2v (dotted line) (n = 2 donors from 2 independent experiments, mean ± SEM). c. Targeting of several T cell subsets and NK cells from fresh PBMCs by PD1-IL2v, FAP-IL2v and FAP-IL2 superkine-analogue (n = 8 healthy donors from 4 independent experiments, box plots representing median, minimum/maximum and individual points). Statistical comparisons were performed using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. d. Frequency of in vitro activated, STAT5-P+ murine CD4 T cells upon exposure for 12 min to increasing concentrations of either muPD1-IL2v or muFAP-IL2v in vitro (n = 2 mice from 2 independent experiments, mean ± SEM.