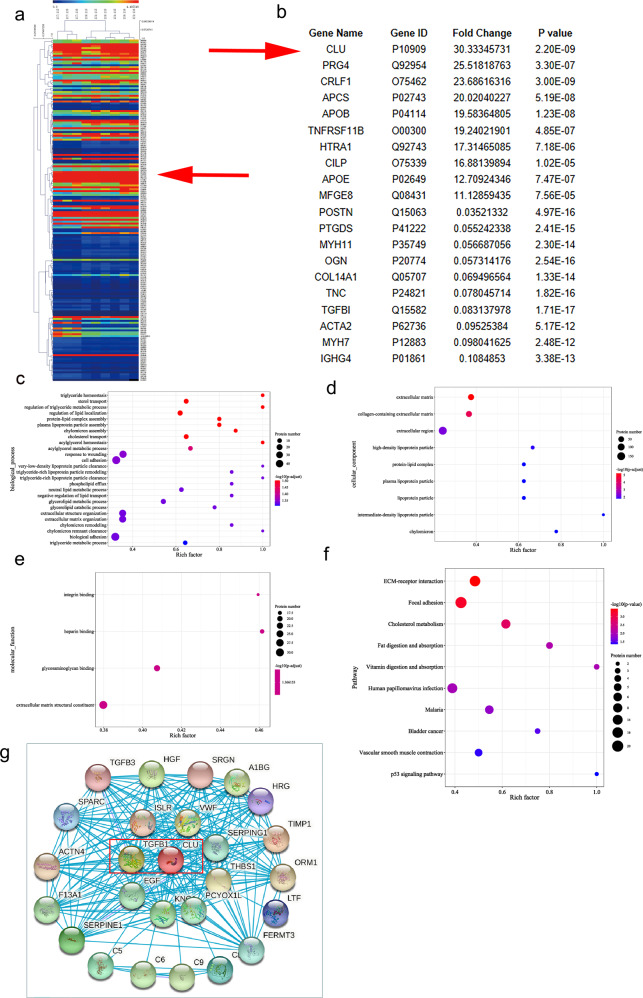
Fig. 1. Proteomic profile of LF as determined by mass spectrometry analysis and bioinformatic analysis.
a A cluster heatmap showing differentially expressed proteins with over 2-fold changes between LFH and non-LFH samples. Red denotes elevated levels, while green denotes decreased levels. Red arrow denotes CLU. b Top 10 up- and top 10 downregulated proteins. Levels of CLU protein in LFH were elevated by >30-fold compared with the control. GO and KEGG pathway analysis. c–e GO terms for differentially expressed proteins (p < 0.05). The color shows the enrichment scores (−lg(p-value)), and the number of proteins tested is proportional to the marker area of the bubble of the significantly enriched GO terms. c Biological process (BP) GO terms. d Cellular component (CC) GO terms. e Molecular function (MF) GO terms. f Pathways associated with differentially expressed proteins in LFH (p < 0.05). g Protein‒protein interaction (PPI) analysis using the STRING tool showing functional association networks of differentially expressed proteins. The associations between nodes are connected with solid lines. Red marked rectangle shows CLU-TGF-β1 interactions.