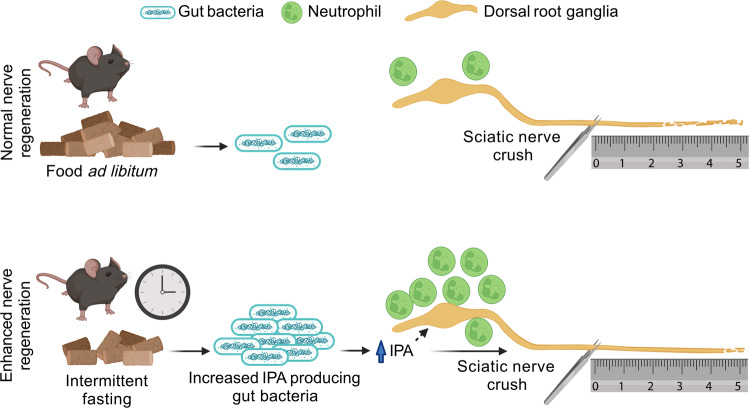
Fig. 1.
Mice receiving food ad libitum (AL) or as an intermittent fasting (IF) diet were subjected to sciatic nerve crush injury. IF led to enhanced nerve regeneration compared to AL feeding. IF was also associated with elevated serum levels of indole-3-propionic acid (IPA) and IPA-producing gram-positive bacteria in the gut. The IF-induced enhanced nerve regeneration was recapitulated with fecal matter transplants from IF mice to AL mice, gut recolonization with Clostridium sporogenes, an IPA-producing bacteria, and systemic IPA delivery. Systemic IPA delivery induced dorsal root ganglia neutrophil infiltration, which was required for IPA enhancement of nerve regeneration. The figure was created with biorender