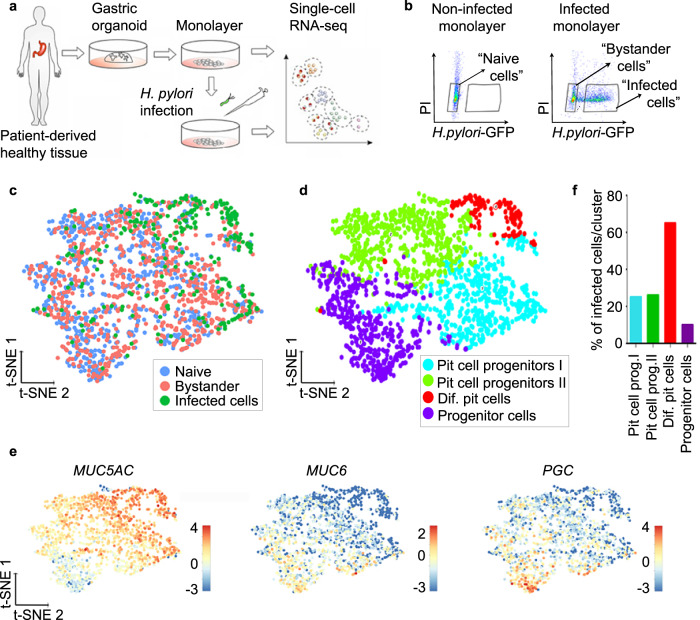
Fig. 2. scRNA-seq reveals that H. pylori binds to a subpopulation of pit cells.
a Scheme of the experimental setup. Gastric organoids were generated from gastric healthy tissue and used to obtain 2D monolayers. Monolayers were infected with GFP-expressing H. pylori (MOI 1) for 6 h and subjected to scRNA-seq. b Representative flow cytometry dot plots of naïve and infected monolayers. Cells were gated as indicated based on GFP signal (H. pylori) and propidium iodide (PI) and subjected to scRNA-seq. c Single-cell transcriptomes from the different gates (panel b) were integrated and projected using a t-distributed stochastic neighbour embedding (t-SNE) 2D projection. The sample origin is colour-coded. d Using known gastric marker genes for the specific gastric cell types, cell identities were assigned. e Expression of known markers specific for pit cells (MUC5AC), neck cells (MUC6) and chief cells (PGC) colour-coded and projected on top of the t-SNE displayed in panels (c) and (d). f Percentage of H. pylori-infected cells per cluster as identified in panel (d).