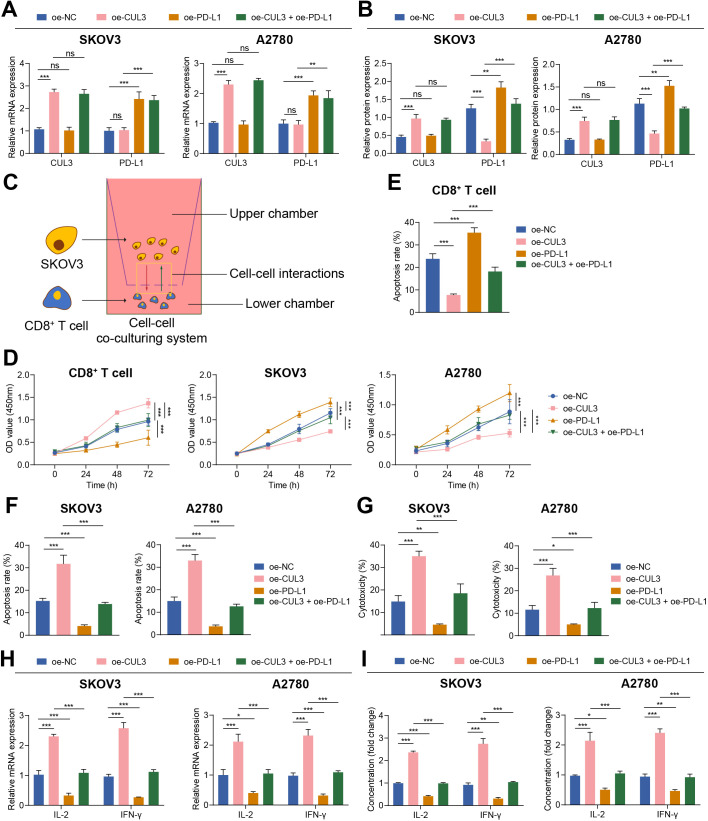
Figure 3.
Overexpression of CUL3 regulated the effect of PD-L1 expression on T cells and ovarian cancer cells. (A) RT-qPCR detection of CUL3 and PD-L1 mRNA levels in SKOV3 and A2780 cells after overexpression of CUL3 or PD-L1. (B) Western blot analysis detection of CUL3 and PD-L1 protein levels in SKOV3 and A2780 cells after overexpression of CUL3 or PD-L1. (C) Transwell for construction of a T cell, SKOV3 and A2780 cell co-culture system. (D) Detection of the proliferation of T cells (left) and SKOV3 (middle) and A2780 cells (right) in the co-culture system by CCK8. (E) Detection of the apoptosis rate of T cells in the co-culture system by flow cytometry. (F) Flow cytometry to detect the apoptosis rate of SKOV3 and A2780 cells in the co-culture system. (G) Lactate dehydrogenase release experiment detected the killing effect of T cells on SKOV3 and A2780 cells. (H) Detection of the changes in the mRNA levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ in each group of T cells in the co-culture system by RT-qPCR. (I) Detection of the changes in the protein levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ in the supernatant in the co-culture system by ELISA. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. All experiments were repeated three times. CUL3, cullin 3; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; mRNA, messenger RNA; PD-L1, programmed death ligand-1; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative PCR.