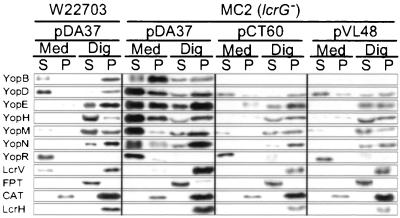
FIG. 2.
lcrG mutant yersiniae display a Los phenotype and secrete effector Yops into the extracellular medium. HeLa cells were infected with Y. enterocolitica W22703 or MC2 (ΔlcrG) harboring plasmids pDA37 (vector control), pCT60 (lcrG), or pVL48 (gst-lcrG). After incubation for 3 h at 37°C, the tissue culture medium (Med) was decanted and centrifuged to separate secreted proteins from those present within nonadherent bacteria. HeLa cells, as well as adherent yersiniae, were extracted with digitonin (Dig), a detergent that solubilizes the eukaryotic plasma membrane but not the bacterial envelope. Extracts were centrifuged to separate proteins solubilized from the HeLa cytoplasm from those that sediment with the bacteria. Proteins were precipitated with chloroform-methanol and analyzed by immunoblotting. Y. enterocolitica MC2 displayed a loss of targeting specificity (Los) and secreted large amounts of YopB, YopD, YopE, YopH, YopM, and YopN into the culture medium. The Los phenotype was complemented by transforming MC2 cells with either pCT60 or pVL48. As a control for proper fractionation, FPT is located in the cytosol of HeLa cells and is solubilized by digitonin extraction. LcrH and CAT reside in the bacterial cytoplasm and are not solubilized by digitonin extraction.