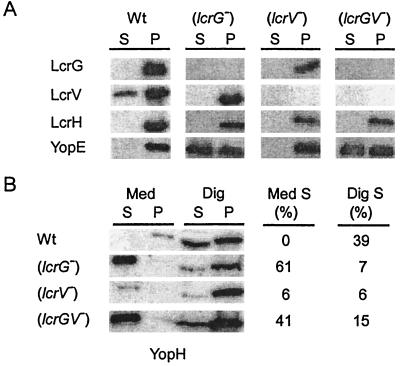
FIG. 3.
lcrGV mutant yersiniae display a calcium-blind and Los phenotype. (A) Y. enterocolitica W22703 (Wt) and the isogenic mutant strains MC2 (lcrG), CT1 (lcrV), and KLD1 (lcrGV) were grown in the presence of calcium for 2 h at 37°C. Cultures were centrifuged, and the supernatant (S) was separated from the cell pellet (P). Protein in each sample was precipitated with TCA, solubilized in sample buffer, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with antisera raised against LcrG, LcrV, LcrH, and YopE. The percentage of secreted YopE is indicated. (B) HeLa cells were infected with Y. enterocolitica strains MC2 (lcrG), CT1 (lcrV), and KLD1 (lcrGV) and incubated for 3 h at 37°C. The tissue culture medium (Med) was decanted and centrifuged to separate secreted proteins from those present within nonadherent bacteria. HeLa cells, as well as adherent yersiniae, were extracted with digitonin (Dig), a detergent that solubilizes the eukaryotic plasma membrane but not the bacterial envelope. Extracts were centrifuged to separate proteins solubilized from the HeLa cytoplasm from those that sediment with the bacteria. Proteins were precipitated with chloroform-methanol and analyzed by immunoblotting with antiserum raised against purified YopH. The percentage of YopH secreted into the extracellular medium (Med S) or targeted into the cytosol of HeLa cells (Dig S) is indicated.