Figure 8. The role of CDK9 and PP2A in transcription termination and RNA maturation.
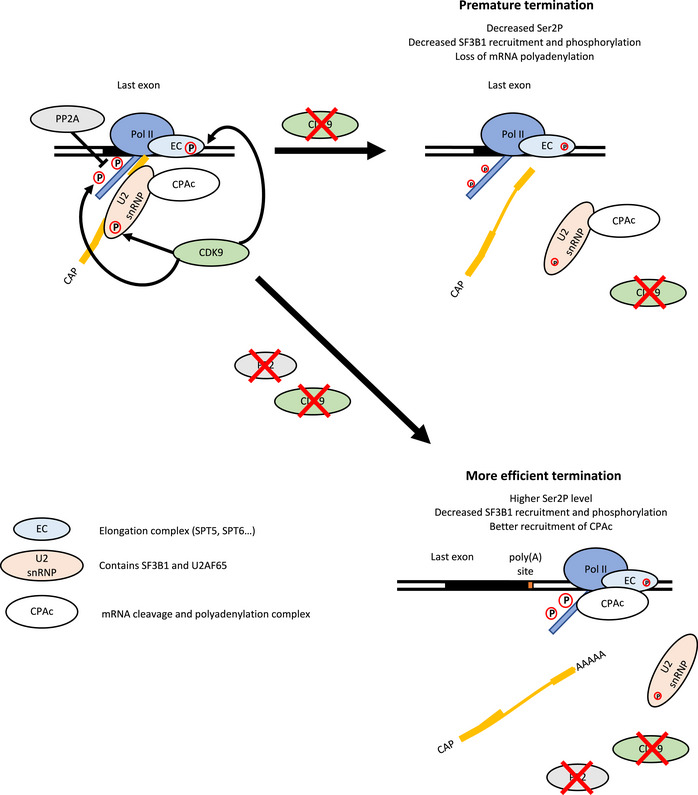
During the transcription cycle, CDK9 phosphorylates the pol II CTD on Ser2 and Ser5, proteins found in the elongation complex, for example, SPT5, and the SF3B1 subunit of the U2 snRNP. The phosphatase PP2A dephosphorylates the pol II CTD on Ser2P and Ser5P. CDK9 inhibition causes a decrease in pol II CTD phosphorylation and proteins found in the elongation complex and loss of the SF3B complex together with CPA factors from pol II, resulting in the premature termination of pol II and loss of polyadenylation. Inhibition of CDK9 and PP2A at the same time results in more phosphorylation of the pol II CTD, but not of SF3B1 T142P. However, PP2A inhibition counteracts the effect of CDK9 inhibition on transcription and mRNA CPA, likely via pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation, resulting in restored mRNA maturation and subsequent transcription termination.
