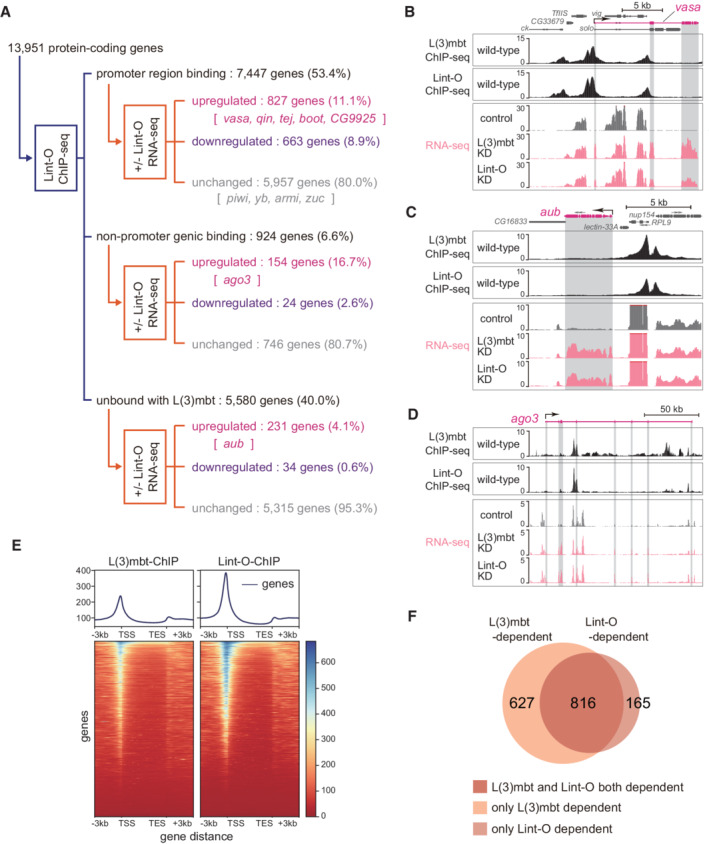
Figure 4. L(3)mbt and Lint‐O share genomic binding to orchestrate gene control in OSCs.
-
AThe 13,951 protein‐coding genes of Drosophila were classified into “promoter region binding,” “nonpromoter genic binding,” and “unbound with Lint‐O” in accordance with the Lint‐O ChIP‐seq reads, and were subsequently divided into “upregulated,” “downregulated,” and “unchanged” in accordance with the RNA‐seq reads from the OSCs before and after Lint‐O depletion (+/− Lint‐O). Representatives of piRNA factors are indicated. ChIP‐seq was performed twice technically and RNA‐seq three times.
-
B–DThe genomic regions harboring vasa (B), aub (C), and ago3 (D) are indicated. The L(3)mbt and Lint‐O ChIP‐seq reads and the RNA‐seq reads from normal (control), L(3)mbt‐depleted, and Lint‐1‐depleted OSCs are shown. The L(3)mbt ChIP‐seq reads and the RNA‐seq reads from normal (control) and L(3)mbt‐depleted were also shown in Fig 1B–D.
-
EHeatmaps show the L(3)mbt ChIP and Lint‐O ChIP scores calculated by deeptools (Ramírez et al, 2016) within each gene body and the extended regions (i.e., 3 kb upstream of the TSS and 3 kb downstream of the TES). The length of all the genes is normalized to be a constant value, 5 kb. The summary plots show the average score.
-
FVenn diagram showing the overlap between L(3)mbt‐ and Lint‐O‐regulated genes.
