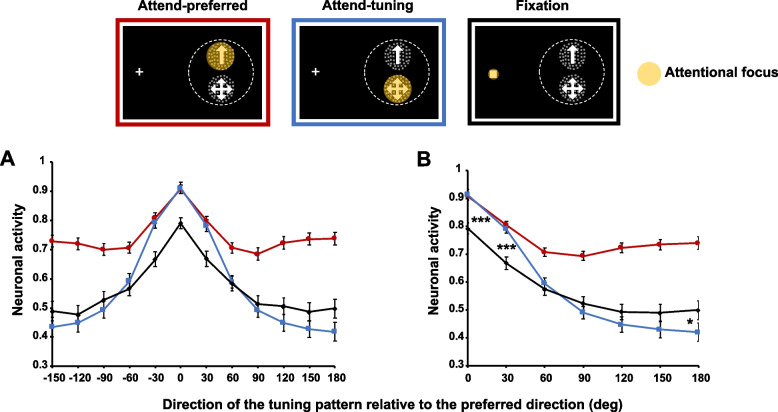
Fig. 2.
A Average normalized neuronal response in each attentional condition. B Normalized neuronal responses averaged across the same (absolute) directional difference (n = 78). Responses in the attend-tuning and the fixation conditions monotonically decrease as the offset between the preferred and tuning patterns increases. Responses in the attend-tuning condition are larger than that in the fixation condition when the direction of the tuning pattern is close to the neuron’s preferred direction (0 ~ 30°). This relationship reverses when the direction of the tuning pattern approaches the neuron’s anti-preferred direction. In the attend-preferred condition, however, responses are lowest when the direction of the tuning pattern is approximately 90° away from the preferred direction. Then, the responses increase as the directional difference increases. Error bars indicate SEM across the normalized responses of each neuron. * p < .05, *** p < .001