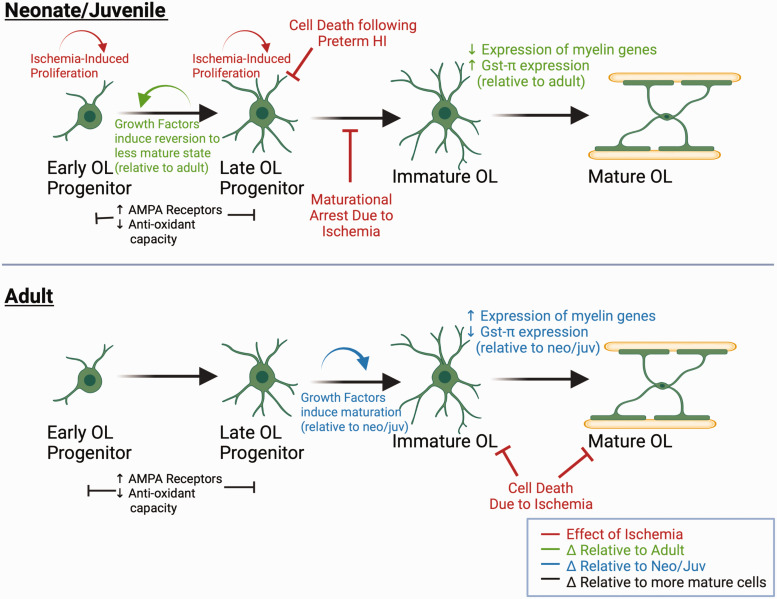
Figure 4.
Age, cellular maturation, and ischemia-induced changes in oligodendrocytes. Both Panels: OPC’s have greater expression of AMPA GluR’s and decreased anti-oxidant proteins and enzymes compared to more mature oligodendrocytes. As oligodendrocytes mature, antioxidant capacity increases due to increased expression of glutathione pathway enzymes. However, there are age-related differences in oligodendrocytes at similar cellular maturational stages. FGF and IGF induce late OPCs from neonatal brains to revert to a less mature state and proliferate (top panel), while late OPCs from adult rodent brains are more likely to differentiate under the same conditions (bottom panel). Immature OL’s in juvenile mice express more GSTπ (top panel) relative to immature OL’s in adult mice (bottom panel). In response to ischemia, late OPCs are selectively vulnerable to cell death, there is rapid proliferation of less mature OPCs (top panel). However, there is maturational arrest of OPCs, limiting remyelination (top panel). In the adult brain, immature and mature OL’s are relatively more vulnerable to ischemia (bottom panel).