Table 3b.
Estimatesa from Six Modelsb of Total Health Care Costs during the Yearc Following COMBINE Treatment Using the COMBINE Economic Study Sample (Categorical Drinking Categories)
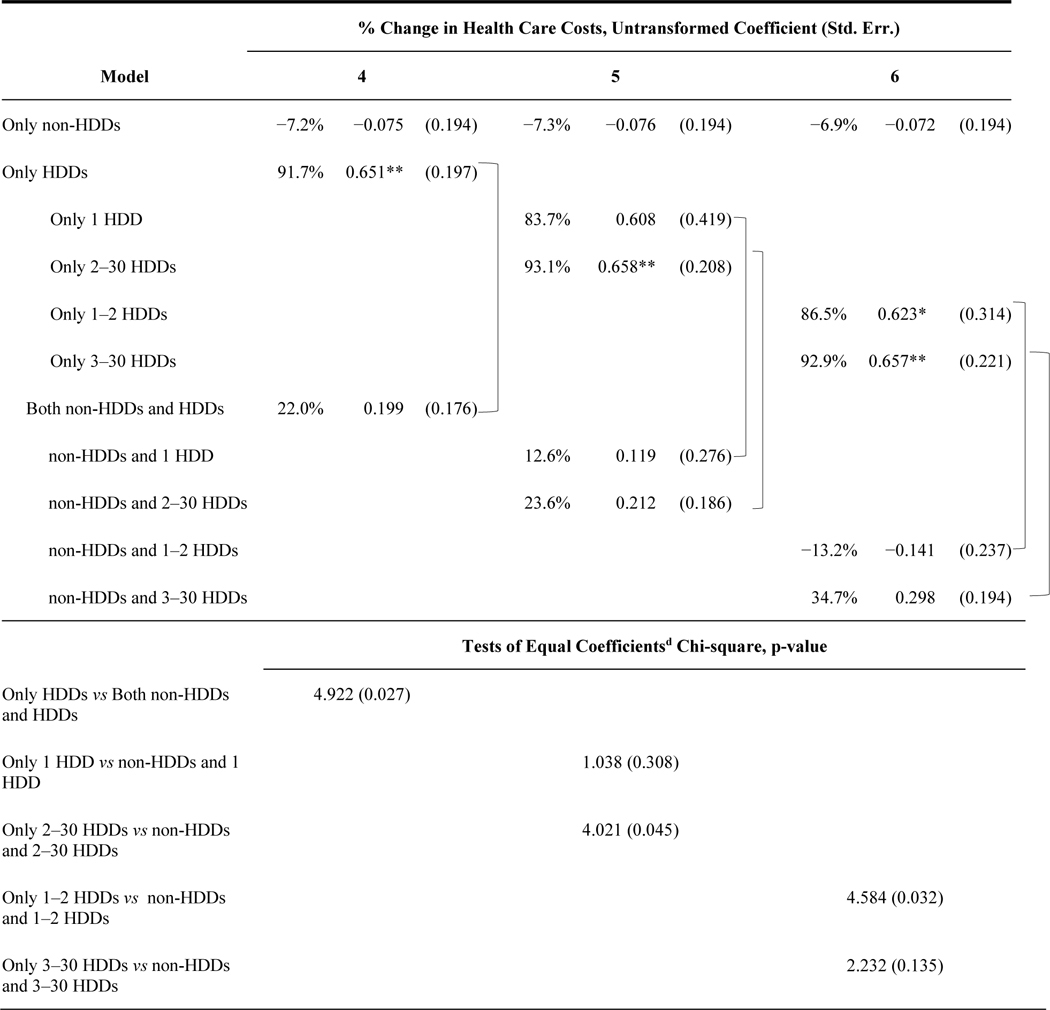
|
p<0.05,
p<0.01 , N=748, Full model results showing the coefficients for these covariates are included in Appendix A.
Estimates are % changes in HC Costs (Incident Rate Ratios – 1) transformed from unadjusted estimates from a GLM with a log-link function and gamma distribution. Robust standard errors for adjusted and unadjusted estimates are in parentheses.
The models comprise three past 30 day Heavy Drinking Day and Non-heavy Drinking Day measures. Heavy drinking days are defined as a day in which 5 or more drinks are consumed for men, 4 or more for women. All other drinking days are defined as Non-heavy Drinking Days.
Based on healthcare use reported from the end of COMBINE treatment through 12 months later.
Wald tests of the null hypotheses for these tests are that the estimated coefficients are equal (Chi-sq distribution, 2 d.f.). Compared coefficients are linked with brackets.
