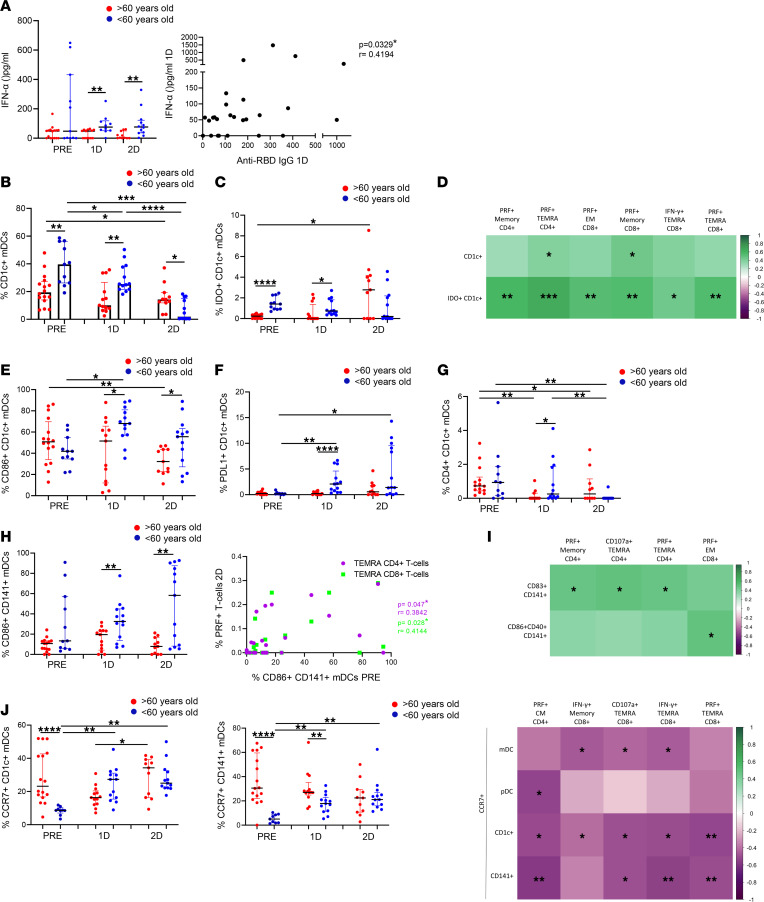
Figure 5. An impaired DC homing and functional capacity are associated with a lower T cell response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in aged people.
(A) Dot plots showing IFN-α production through CpG-A stimulation for 18 hours in > 60-year-old (red) and < 60-year-old (blue) participants before SARS-CoV-2 vaccination (PRE), 3 weeks after the first dose (1D), and 2 months after the second dose (2D) (left). Correlation analysis of IFN-α production with anti–RBD IgG levels 3 weeks after the first dose of vaccination (right). (B and C) Bar graphs representing the percentage of CD1c+ and IDO+CD1c+ mDCs in > 60-year-old (red) and < 60-year-old (blue) participants at the 3 follow-up time points. (D) Correlation matrix showing associations between the percentages of CD1c+ mDCs and IDO+CD1c+ mDCs before vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 S–specific T cells expressing cytokines or cytotoxicity markers 2 months after the second dose. (E–G) Dot plots showing the percentage of CD1c+ mDCs expressing CD86 (E), PD-L1 (F), and CD4 (G) in > 60-year-old (red) and < 60-year-old (blue) participants at the 3 time points. (H) Dot plots showing the percentage of CD141+ mDCs expressing CD86 (left) in > 60-year-old (red) and < 60-year-old (blue) participants at the 3 time points. Correlation plot between the percentage of CD86+CD141+ mDCs before vaccination and the percentage of S-specific PRF+ TEMRA CD4+ and CD8+ T cells 2 months after the second dose (right). (I) Correlation matrix showing associations between the percentage of CD141+ mDCs expressing activation markers after TLR-3 stimulation for 24 hours with SARS-CoV-2 S–specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing cytotoxicity markers. (J) Dot plots showing the percentage of CCR7+ mDCs in > 60-year-old (red) and < 60-year-old (blue) participants in the 3 follow-up time points (left and middle panels), and a correlation matrix representing associations of the percentage of mDCs expressing CCR7 with SARS-CoV-2 S–specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing cytokines or cytotoxicity markers 2 months after the second dose (right panel). Mann-Whitney U (A, B, C, E, F, G, H, and J), Wilcoxon (A, B, C, E, F, G, H, and J), and Spearman (A, D, H, I, and J) tests were used (n = 32). Friedman test was applied in A (> 60-year-old, P = 0.801; < 60-year-old, P = 0.717), B (> 60-year-old, P = 0.169; < 60-year-old, P = <0.0001), C (> 60-year-old, P = 0.147; < 60-year-old, P = 0.027), E (> 60-year-old, P = 0.018; < 60-year-old, P = 0.086), F (> 60-year-old, P = 0.381; < 60-year-old, P = 0.013), G (> 60-year-old, P = 0.042; < 60-year-old, P = 0.034), H (> 60-year-old, P = 0.223; < 60-year-old, P = 0.234), and J (CD1c mDCs: > 60-year-old, P = 0.121; < 60-year-old, P = 0.001 and CD141 mDCs: > 60-year-old, P = 0.459; < 60-year-old, P = 0.001).