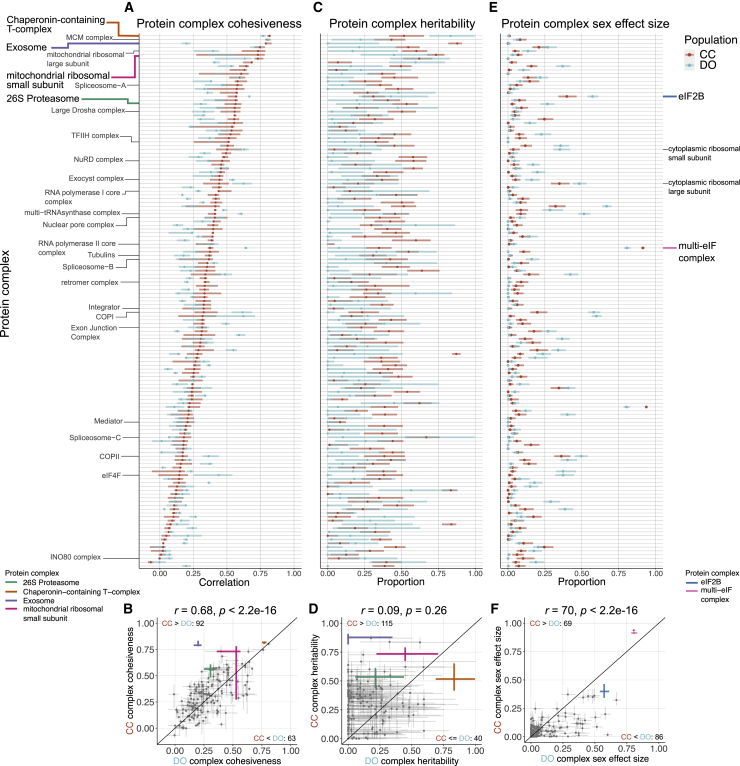
Figure 3.
Genetic and sex effects on protein complexes
(A and B) Complex cohesiveness, the median pairwise Pearson correlation among members, for CC (red) and DO (blue) mice for 163 protein complexes. Intervals represent the interquartile range, and points represent the overall median.
(C–F) Complex heritability (C and D) and complex sex effect size (E and F), the proportion of variance in PC1 explained by sex, are estimated using the first principal component (PC1) from each of the protein complexes. Intervals represent 95% subsample intervals (STAR Methods). The exosome, CCT complex, 26S proteasome, and MRSS are highlighted as examples of protein complexes with unique genetic effects patterns (Figures 4, 5, 6, S5, and S6). The multi-eIF complex and eIF2B are highlighted as complexes with large sex differences in CC and DO mice. The identity line is included for reference. Pearson correlation coefficients (r) between CC and DO mice and corresponding p values included.