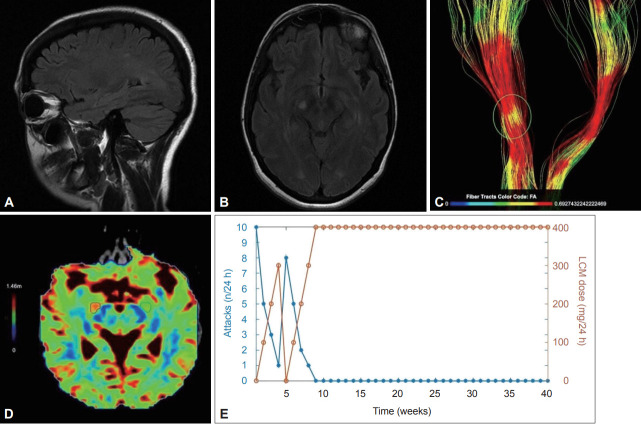
Figure 1.
Brain MRI examination was performed on a 3T system (Siemens Magnetom Vida 3T, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) using a 64-channel head coil. Anatomical imaging based on a 3D T1-weighted sequence was acquired using an MPRAGE sequence (voxel-size 1 × 1 × 1 mm, sagittal slice, orientation, matrix size 240 × 240). DTI acquisition included an axial single-shot spin-echo echoplanar imaging sequence with 32 diffusion encoding directions (field of view: 240 × 240 mm, acquisition voxel size: 2 × 2 × 2 mm, sensitivity encoding reduction factor of 2, multislice acceleration factor of 2, two b factors with 0 s/mm2 (low b), and 1,000 s/mm2 (high b), scan time was 2 min 36 s). DTI tractography analysis comprised the examination of white matter tracts as 3-dimensional and quantitative data of white matter fibers (corticospinal tract, inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, corpus callosum). The Brainance DTI suite (Advantis Medical Imaging, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) was used for the reconstruction and visualization of 3-dimensional white matter tracts and the extraction of quantitative data (apparent diffusion coefficient, fractional anisotropy, radial diffusivity). A and B: Axial and sagittal FLAIR MRI scans of the brain show a hyperintense lesion in the right cerebral peduncle along with scattered hyperintensities in the subcortical and periventricular white matter, primarily in the vicinity of the trigones of the lateral ventricles. C: Reconstruction of the corticospinal tracts with color encoding based on the variations in FA. The area of the pathology is highlighted, and a reduction in FA is observed related to disorganized tracts. D: Color encoded map of radial diffusivity. The area with high signal intensity is mapped with red color visualizing the extension of the total area close to the lesion with a 20.7% increase in radial diffusivity compared to the green marked contralateral region of interest with normal values. Radial diffusivity reflects diffusivity perpendicular to axonal fibers and appears to be more strongly correlated with myelin abnormalities, either dysmyelination or demyelination. E: The relationship between LCM dose and the frequency of the attacks. Significant remission of the attacks was achieved within 3 days of initiating low-dose LCM, which was subsequently uptitrated to 300 mg daily, leading to almost complete cessation of the attacks. After an episode-free period, LCM was abruptly discontinued, leading to recurrence of the attacks (up to eight per day), thereby proving that the declining frequency of the attacks in the first four weeks was casually linked to LCM rather than to the natural course of PKD. Ten months later, the patient remained free of attacks with 400 mg LCM daily. DTI, diffusion tensor imaging; FA, fractional anisotropy; LCM, lacosamide; PKD, paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia.