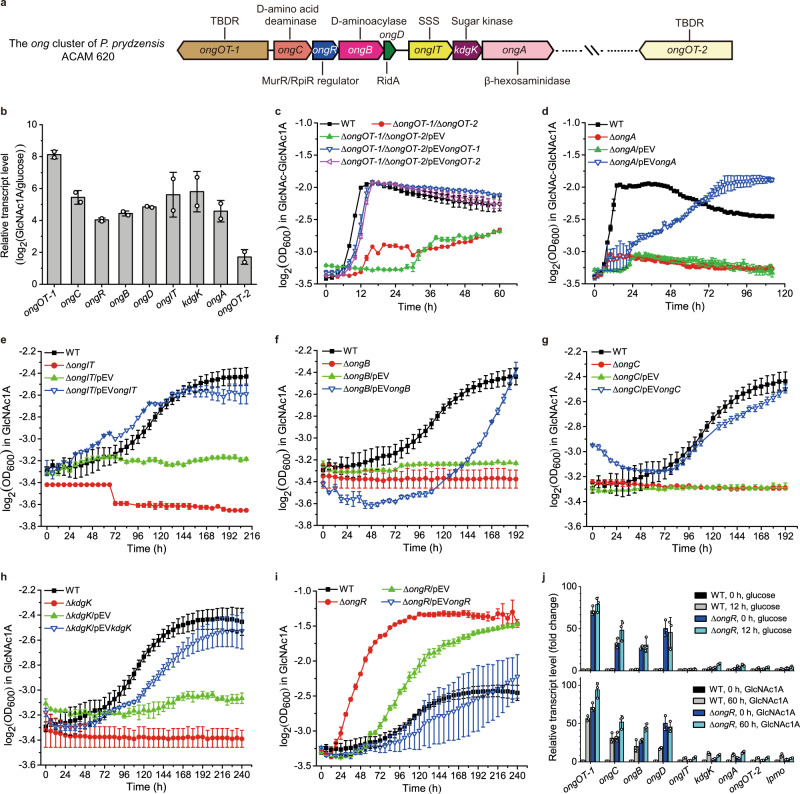
Fig. 3. Identification of key genes in strain ACAM 620 involved in utilizing oxidized chitooligosaccharides based on transcriptomic and genetic analyses.
a Genetic organization of the ong cluster of strain ACAM 620. TBDR, TonB-dependent receptor; SSS, sodium solute symporter. b RNA-seq assay of the transcriptions of genes from the ong cluster and ongOT-2 in strain ACAM 620 in the minimal medium supplemented with 0.2% (w/v) GlcNAc1A. Values are expressed as fold change (log2) compared to cultures in the minimal medium supplemented with 0.2% (w/v) glucose. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 2 independent experiments). c–i The growth phenotype of strain ACAM 620 with a single gene deletion in the ong cluster on GlcNAc1A or GlcNAc-GlcNAc1A as the sole carbon source. Wild-type strain (WT), mutant strains and complemented strains of mutants were grown at 25 °C in the minimal medium supplemented with 10 mM GlcNAc1A or 10 mM GlcNAc-GlcNAc1A. Deletion mutant strains with the empty plasmid pEV were used a control. The y-axes in c-i represent log2 transformation of the OD600 value. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 2 independent experiments). j, RT-qPCR assay of the transcriptions of lpmo, ongOT-2 and genes from the ong cluster in the WT and △ongR mutant strains in response to 0.2% (w/v) glucose (upper) or 0.2% (w/v) GlcNAc1A (lower) in the minimal medium. Values are expressed as fold change compared to precultures of the WT strain in the minimal medium supplemented with 0.2% (w/v) glucose. The rpoD gene was used as an internal reference. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.