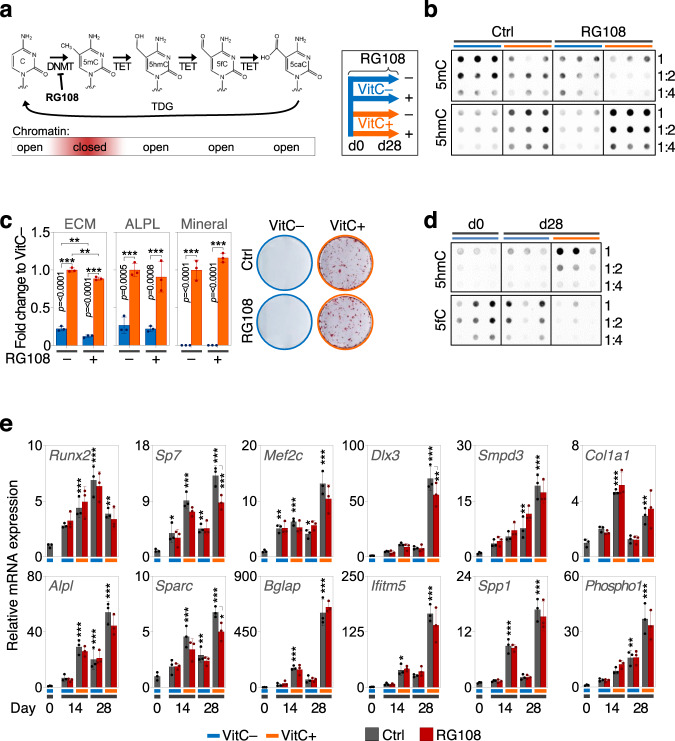
Fig. 9. Vitamin C-induced 5hmC is a stable epigenetic mark that is required for osteogenic differentiation.
a Schematic representation of the active DNA demethylation cycle and experimental design for the shown experiments in differentiating osteoblasts. b Dot blots at day 14 with and without VitC and/or the DNMT-inhibitor RG108, which decreases global CpG methylation levels (5mC). c ECM deposition, alkaline phosphatase activity (ALPL) and ECM mineralization in the presence or absence of VitC and/or RG108. d Dot blots for 5hmC and 5fC (formyl-cytosine) in osteoblasts at indicated time points in the presence or absence of VitC. e Osteoblastic gene expression after VitC and/or RG108 administration. Bar graphs represent mean ± SD; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Two-way ANOVA analysis with Sidak’s multiple comparison tests (c and e), groups compared to day 0 Ctrl or as marked in e. In c, for ECM RG108- VitC- vs RG108 + VitC- **p = 0.0062 and RG108- VitC+ vs RG108 + VitC + **p = 0.0029. N = 3 (c, e) per group, from biologically independent experiments. Source data as well as exact p = values for all comparisons in (e) are provided in the Source Data File.