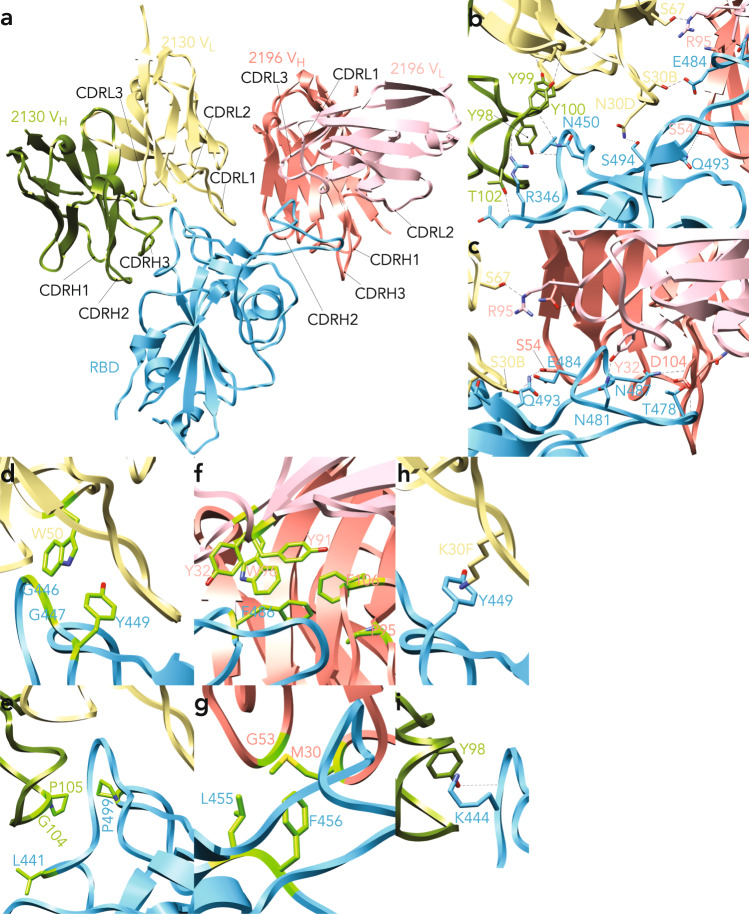
Fig. 7. Structural details of the diverse interactions between in vivo-produced dFabs and the SARS-CoV-2 (USA-WA1/2020) spike trimer.
a Structural overview of RBD (blue) in complex with both 2196 (VL in pink; VH in salmon) and 2130 dFabs (VL in gold; VH in green). b 2130 interactions with RBD main chain partners (CDRH3 T102 to RBD R346 peptide bond; RBD 346 to CDRH3 Y100 peptide bond; CDRH3 Y98 top to RBD V445 peptide bond; RBD N450 to CDRH3 Y100 peptide bond) and side chain partners (CHRL1 N30 to RBD S494 and CDRL1 to S30B to RBD 484E). c 2196 interactions with RBD (Q493 engages CDRH2 S54, RBD N481 engages CDRL1 Y32, RBD N487 engages CHRL3 D104 and RBD T478 engages CHRL3 D104). d, e 2130 interactions with RBD via hydrophobic interactions. d CDRL2 W50 packs against RBD G446, G447 and Y449. e CDRH3 G104-P105 packs against RBD L441 and P499. f, g 2196 interacts with RBD via hydrophobic interactions: f hydrophobic cage with RBD F486 formed by CDRL1 Y32, CDRL3 Y91 and W96, CDRH3 P95 and F106. g additional hydrophobic contacts include CDRH1 M30, CDRH2 G53 and RBD L455 and L456. h-i Cation-pi interactions between 2130 and RBD: h CDRL1 30F to RBD Y449. i CDRH3 Y98 to RBD K444.