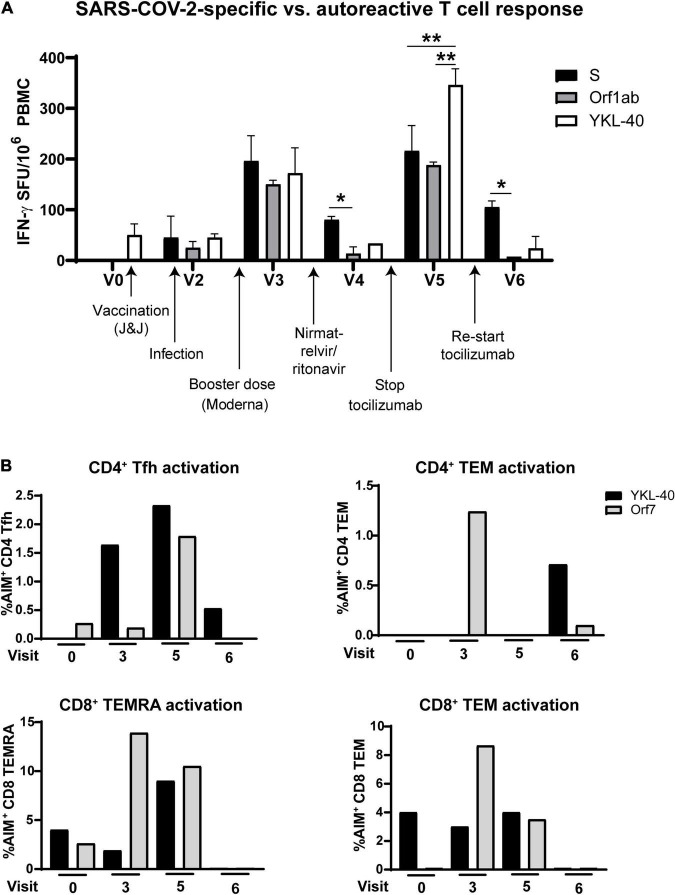
FIGURE 4.
Autoreactive T cell responses oscillate in coordination with SARS-CoV-2-specific responses after infection. (A) T cell production of IFN-γ after stimulation with rheumatoid arthritis-associated cartilage autoantigen YKL-40 compared with Spike- and Orf1ab-specific activation. (B) Activation of T cell subsets over the course of the study after stimulation with the rheumatoid arthritis-associated antigen YKL-40 or SARS-CoV-2 Orf7 peptides. Stopping tocilizumab resulted in increased virus-specific and autoreactive T cell reactivity, while resuming tocilizumab suppressed autoreactivity in most T cell subsets. Data representative of 2 individual experiments, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test.