Fig. 2.
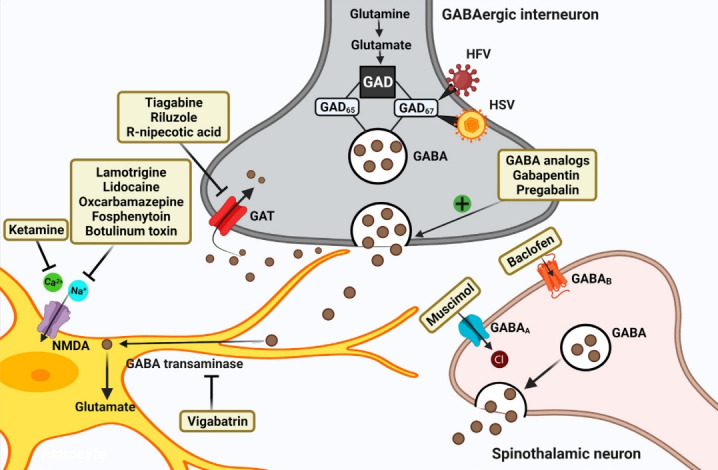
Schematic representation of strategies targeting GABAergic system for attenuating chronic neuropathic pain post-spinal cord injury (SCI). Restoring the hypoactive inhibitory GABAergic tone favors analgesia post-SCI. GABA analogs remain the firstline treatment. Other strategies include inhibiting GABA transporter, GABA transaminase enzyme, Ca2+, and Na+ channels. Current therapies focus on gene therapies using viral vectors that encode GAD enzyme synthesizing GABA. GAD, glutamate acid decarboxylase; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; GAT, GABA transporter; HFV, human foamy virus; HSV, herpes simplex virus.
