FIGURE 8.
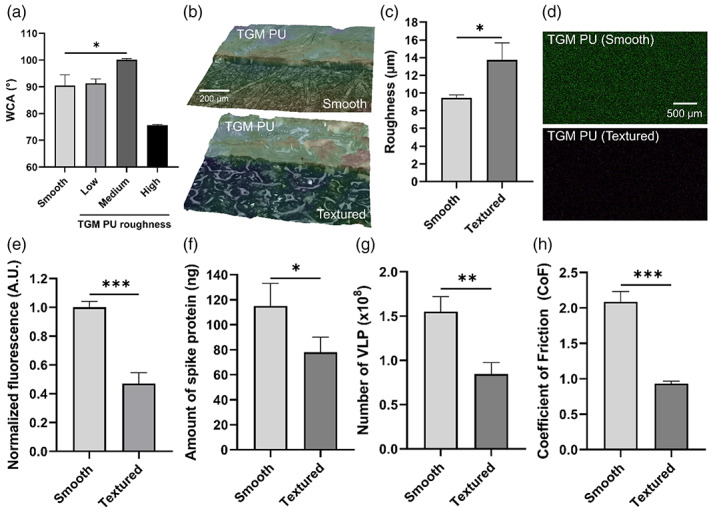
Surface modification of TGM PU for enhanced functionality of FlexiPalm. (a) WCA measurements of TGM PU and surface‐modified TGM PU with microtextures generated by casting on 800, 360, and 60 grit sandpaper, annotated by low, medium, and high roughness, respectively. (b) Laser scanning microscopy images of TGM PU (smooth) and TGM PU (textured) with increased surface roughness. (c) Quantification of the surface roughness between TGM PU (smooth) and TGM PU (textured). (d) Epi‐illumination images of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein‐FITC adsorbed on TGM PU (smooth) and TGM PU (textured) over a 2‐hour incubation period. (e) Quantification of the amount of bound SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein in (d) based on FITC fluorescence intensity. (f and g) The amount of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein (f) and VLP (g) recovered in the eluent after being rinsed off from the TGM PU (smooth) and TGM PU (textured) as quantified by ELISA. (h) Reduced CoF in TGM PU (textured) as compared to TGM PU (smooth). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001. CoF, coefficient of friction; PU, polyurethane; VLP, virus‐like particles; WCA, water contact angle
