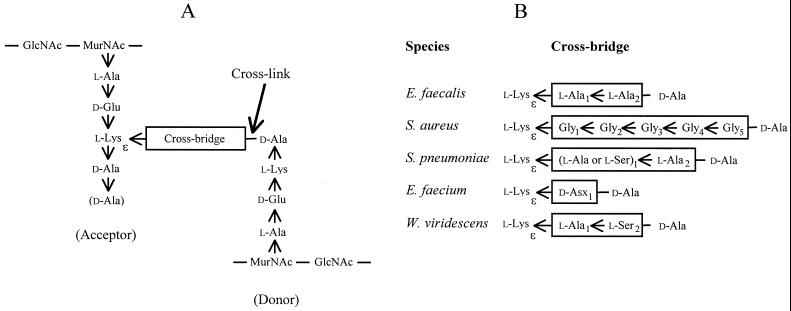
FIG. 1.
Structure of cross-linked peptidoglycan. (A) Fragment of the primary structure of peptidoglycan. The position of the peptide bond formed by the d,d-transpeptidases (penicillin-binding proteins) between the acceptor and donor peptide stems is indicated (cross-link). The C-terminal d-Ala residue of the pentapeptide acceptor stem (shown in parentheses) is generally cleaved by d,d-carboxypeptidases. (B) Sequence of the cross bridges in various bacterial species. The amino acid residues are added to the ɛ-amino group of l-Lys of peptidoglycan precursors by various ligases discussed in the text. d-Asp is incorporated into the peptidoglycan precursors of E. faecium and is secondarily partially amidated (d-Asx may be d-Asp or d-Asn), according to Schleifer and Kandler (19). Arrows indicate CO→NH orientation of peptide bonds.