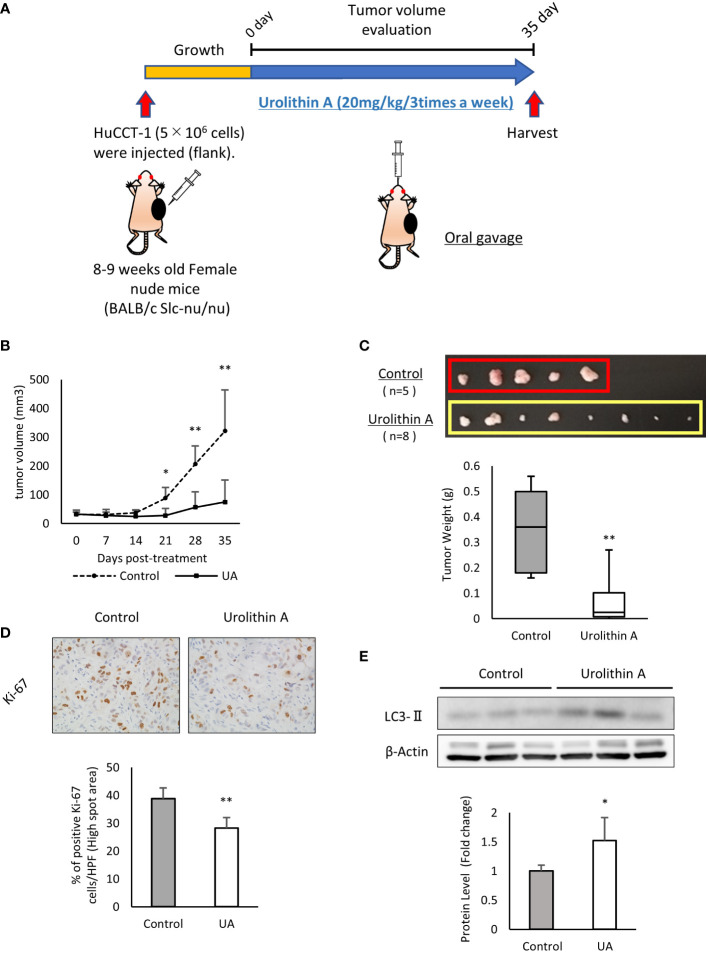
Figure 4.
UA inhibits xenograft tumor growth in vivo. (A) Experimental design for UA treatment in the xenograft model. HuCCT-1 cells were injected into the flank of nude mice. UA (20 mg/kg, 3 times a week) or DMSO (control) were administered by oral gavage for 35 days. (B) The volume of subcutaneous tumors in the xenograft model was measured twice a week. Data represent the means of the control group (n = 5) or the UA group (n = 8). Bars, standard deviation; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (C) Representative macroscopic images of tumors in nude mice obtained at day 35 after the start of the treatment. Data represent the means of the control group (n = 5) or the UA group (n = 8). Bars, standard deviation; **P < 0.01. (D) Representative Ki67-stained immunohistochemical images of the two groups. The positive rates of Ki67 staining were quantified by measuring five high spot areas from each tumor. Data represent the means of the control group (n = 4) or the UA group (n = 4). Bars, standard deviation; **P < 0.01. (E) Autophagy was detected by Western blotting for LC3-II in the two groups. β-actin was used as an internal loading control. LC3-II levels were normalized against β-Actin and represented the means of three independent experiments. Bars, standard deviation; *P < 0.05.