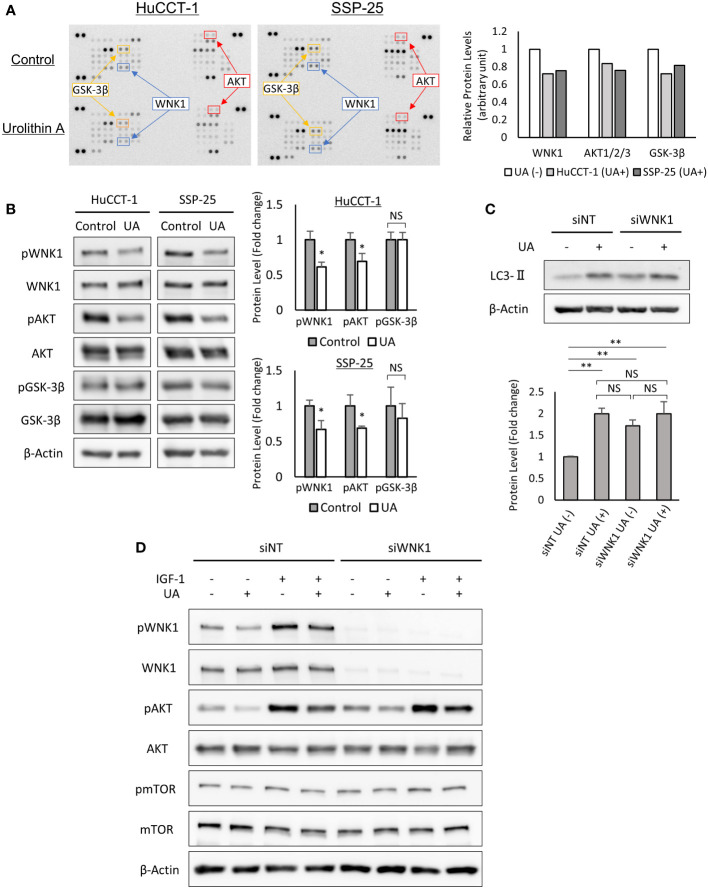
Figure 5.
UA treatment downregulated AKT and WNK1 pathways, and induced autophagy in cholangiocarcinoma cells. (A) HuCCT-1 and SSP-25 cells were treated with 40 μmol/L UA for 3 h and analyzed using the human Phospho-Kinase array. Relative levels of protein phosphorylation (normalized intensity for each antibody) were quantified as a ratio of the UA-treated sample to the untreated one. (B) Results of the human Phospho-Kinase array were verified by Western blotting. β-actin was used as an internal loading control. Protein phosphorylation levels were normalized against β-Actin and represented the means of three independent experiments. Bars, standard deviation; NS, not significant; *P < 0.05. (C) Western blotting for LC3-II in WNK1 knocked down HuCCT-1 cells. Cells were treated with 40 μmol/L UA for 24 h β-actin was used as an internal loading control. LC3-II levels were normalized against β-Actin and represented the means of three independent experiments. Bars, standard deviation; NS, not significant; **P < 0.01. (D) Western blotting for WNK1 (Thr60 and total), mTOR (Ser2448 and total), and AKT (Ser473 and total) in HuCCT-1 cells transfected with control (siNT) or WNK1-specific (siWNK1) small interfering RNAs. Cells were treated with 40 μmol/L UA and 50 ng/mL IGF-1 for 3 h.