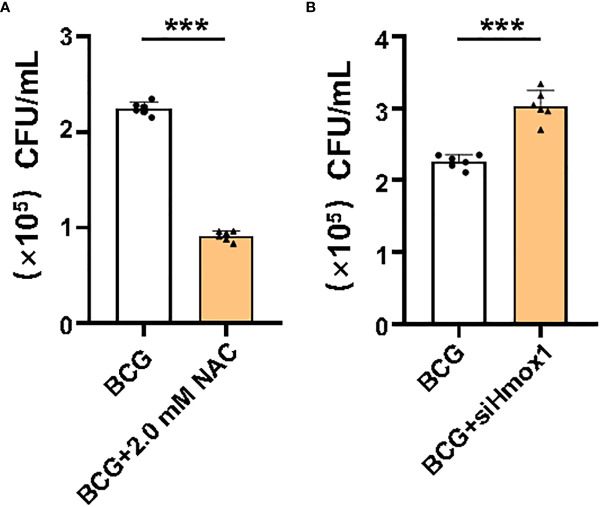
Figure 7.
Effect of ROS and Hmox1 on intracellular bacterial loads in RAW264.7 macrophages. Intracellular ROS was scavenged by NAC treatment, and the expression of Hmox1 was inhibited by the transfection of siRNA to Hmox1. NAC-pretreated or si-Hmox1-transfected RAW264.7 macrophages were incubated with BCG at an MOI of 5 for 1 h, and cells were rinsed to remove uninfected bacteria prior to being cultured with fresh medium for an additional 24 h. The bacteria released in the culture medium was counted by CFU assay. (A) The count of colonies in medium of cells pretreated with NAC. (B) The count of colonies in medium of cells transfected with si-Hmox1. The NAC pretreatment significantly reduced bacteria released from cell necrosis/ferroptosis death, while si-Hmox1-mediated knockdown of Hmox1 gene strikingly increased CFU count in RAW264.7 cells infected with BCG. Data obtained from three independent experiments were processed using GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 software. Unpaired t-test was used to analyze the differential changes of the two groups. ***p < 0.001; n = 3.