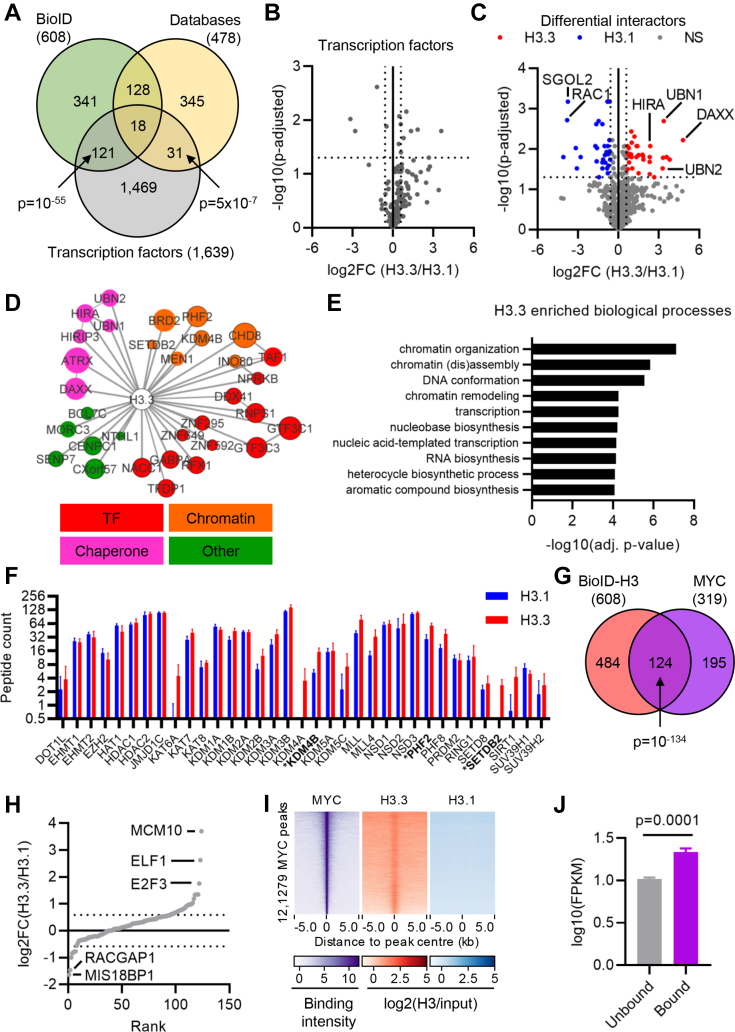
Fig. 3.
The H3.3-specific interactome converges on transcriptional regulators.A, Venn diagram comparing BioID and STRING/BioGRID H3 interactors with human transcription factors (TFs). p-values: hypergeometric test. B, volcano plot comparing TF association with H3.3 and H3.1. C, volcano plot comparing differential interaction between H3.3 and H3.1, highlighting those passing a cut-off of absolute log2FC >1.5 and adjusted p-value <0.05 in blue (H3.1) and red (H3.3). D, network of H3.3-specific interactors colored by to function (red, TFs; orange, chromatin; pink, histone chaperone; green, other). Node size reflects peptide count. Edges between nodes denote protein–protein interactions between the proteins with edge weight denoting confidence. E, biological processes enriched among H3.3-specific interactors. F, peptide counts from BioID for histone modifiers (n = 4). Bars show mean ± standard deviation. G, Venn diagram comparing BioID H3 interactors with MYC-interacting proteins. H, MYC interacting proteins ranked by log2(H3.3/H3.1). Dotted lines mark log2FC = 1.5 and −1.5. I, ChIP-Seq enrichment of MYC, H3.3, and H3.1 in regions ±5 kb around the centre of MYC binding sites in HeLa cells. J, mean expression of genes bound or not by MYC in HeLa-S3 cells (n = 4). ChIP-Seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing.