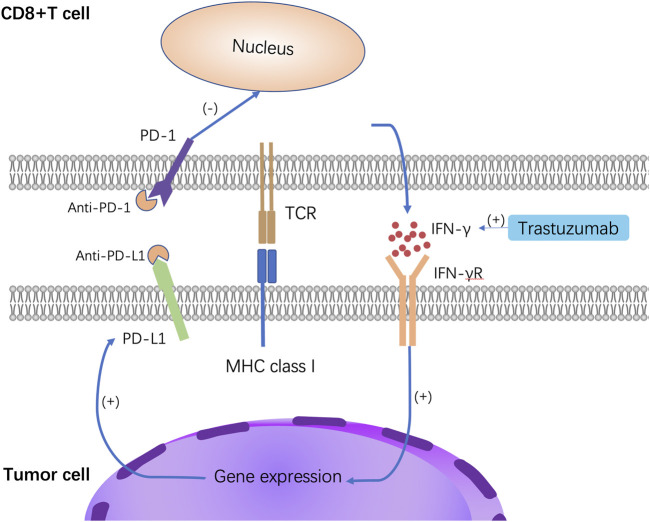
FIGURE 3.
Mechanism of anti-PD-L1 therapy. After interferon exposure, tumor cells reactively express PD-L1, which binds to PD-1 on the surface of T cells and inhibits T cells. Anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies can block the interaction of PD-1 with PD-L1 and reverse the inhibition of CD8+ T cells, thereby enhancing anti-tumor activity.