Figure 4.
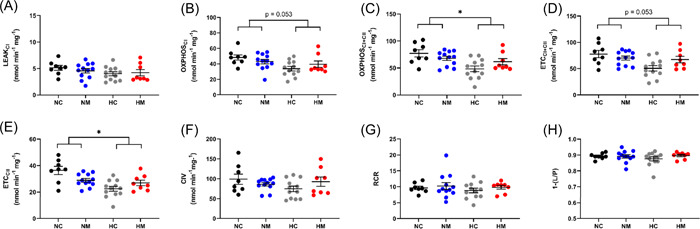
Developmental hypoxia reduces oxidative capacity in heart mitochondria from male fetuses at multiple points of the electron transport chain. Mitochondrial oxidative capacity was measured following a SUIT protocol. Each panel represents a different respiratory state. RCR values (G) and coupling efficiencies (H) were high for all groups, demonstrating mitochondrial homogenate preparations were of good quality. n = 8 (NC from 6 litters), 12 (NM from 7 litters), 12 (HC from 7 litters), 8 (HM from 6 litters). *p< .05 (effects of hypoxia). Significance was assessed using a linear mixed model (nested). Error bars show mean ± SEM. 1‐(L/P), coupling efficiency; CI, complex I; CII, complex II; CIV, complex IV; ETC, electron transport capacity; HC, hypoxia control; HM, hypoxia melatonin; NC, normoxia control; NM, normoxia melatonin; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; RCR, respiratory control ratio; SUIT, substrate–uncoupler–inhibitor–titration.
