Figure 3.
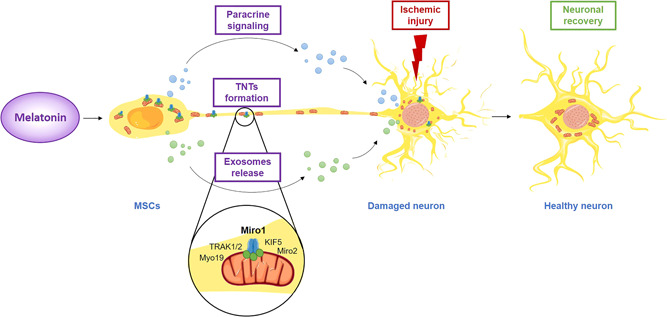
Melatonin as a potential modulator in mesenchymal stem cell communication and neuronal recovery. Melatonin has a variety of effects on MSCs, which include paracrine signaling through modulation of the inflammatory microenvironment or secretion of survival‐promoting neurotrophic factors, exosomes release, and TNTs formation. TNTs transport a variety of cellular components, including organelles, proteins, calcium ions, viruses, and bacteria. This representation highlights the new role of melatonin as a promising agent able to promote mitochondrial transfer via TNTs in MSCs leading to neuronal recovery. KIF5, kinesin‐related protein 5; Miro1, mitochondrial Rho‐GTPase 1; Miro2, mitochondrial Rho‐GTPase 2; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; Myo19, myosin XIX; TNTs, tunneling nanotubes; TRAK1/2, trafficking kinesin‐binding protein 1 and 2
