Figure 7. The HFD and osmotic mini pump‐infused STZ model dose‐dependently alters peripheral hypersensitivity to touch stimulus and reduces the number of epidermal nerve fibres in rear paw glabrous skin.
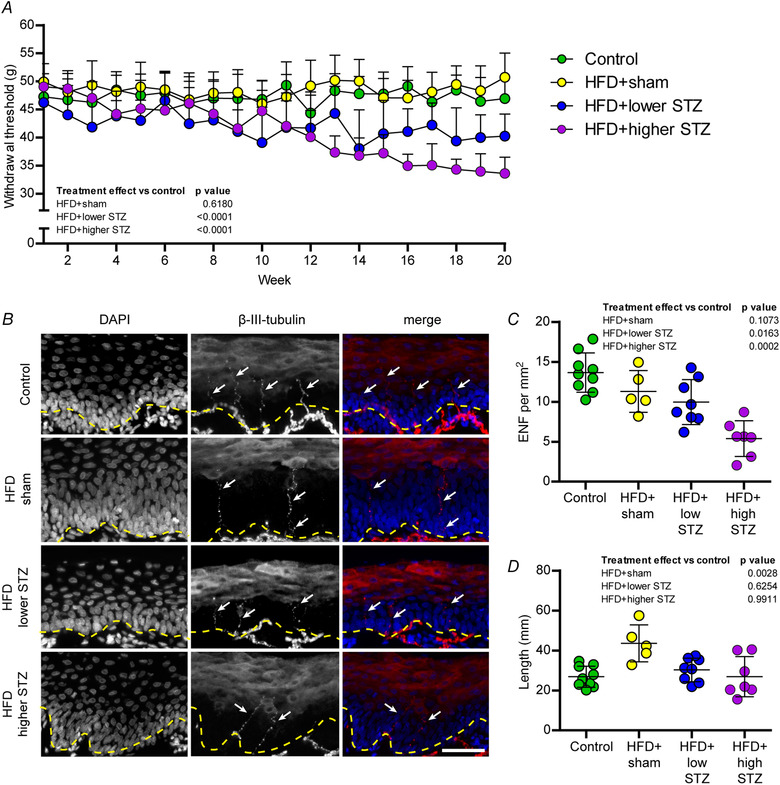
A, pressure required to stimulate voluntary paw withdraw (withdrawal threshold) was assessed weekly using a plantar aesthesiometer. Each data point represents the average for each group and is the combined response from three separate assessments per animal per week. B, rear paw glabrous skin was collected in week 21 and cryosectioned for immunohistochemical analysis of epidermal nerve fibre density using β‐III‐tubulin (arrows). Counterstaining was performed using DAPI to visualise nuclei, allowing identification of the epidermal border (dashed line). Scale bar = 50 μm. C, number of epidermal nerve fibres per mm2. D, length of epidermal nerve fibres was assessed in each animal. In (A), data are the mean ± SD for n = 9 in control; n = 9 in HFD + sham; n = 13 in HFD + lower STZ; and n = 9 in HFD + higher STZ. In (A), two‐way repeated measures ANOVA with Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc was used to analyse data. Individual points in (C) and (D) represent individual animals. In (C) and (D), one‐way ANOVA with Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc was used to assess differences between groups. P values are main effects of treatment vs. the control group. Within and between group interactions are outlined in the Results section. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
