Fig. 2.
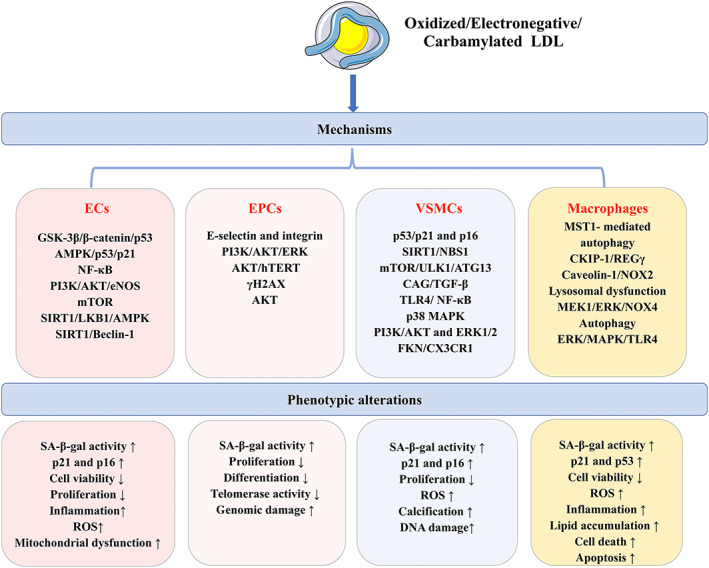
Cellular senescence of various types of cells induced by low‐density lipoprotein (LDL). LDL is a strong pro‐atherogenic lipoprotein, especially in its modified forms oxidized LDL, electronegative LDL and carbamylated LDL. They can lead to the senescence of endothelial cells (ECs), endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and macrophages via activation of multiple signalling pathways related to oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy. The phenotypic profiles of these senescent cells are functionally impaired, resulting in atherosclerosis. AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate‐activated protein kinase; ATG13, autophagy‐related protein 13; CAG, glycosaminoglycan; CKIP‐1, casein kinase 2‐interacting protein‐1; CX3CR1, C‐X3‐C motif chemokine receptor 1; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinase; FKN, Fractalkine; GSK‐3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; γH2AX, phosphorylated histone protein H2AX; hTERT, human telomerase reverse transcriptase; LKB1, liver kinase B1; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; MEK1, mitogen‐activated protein kinase 1; MST1, mammalian ste20‐like kinase 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NBS1, Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome‐1; NF‐κB, nuclear factor kappa‐B; NOX, NADPH oxidase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3‐kinase; REGγ, 11S regulatory particles, 28 kDa proteasome activator, proteasome activator subunit 3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SA‐β‐gal, senescence‐associated β‐galactosidase; SIRT1, silent information regulator 1; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor β; TLR4, toll‐like receptor 4; ULK1, Unc‐51 like autophagy activating kinase 1.
