Fig. 3.
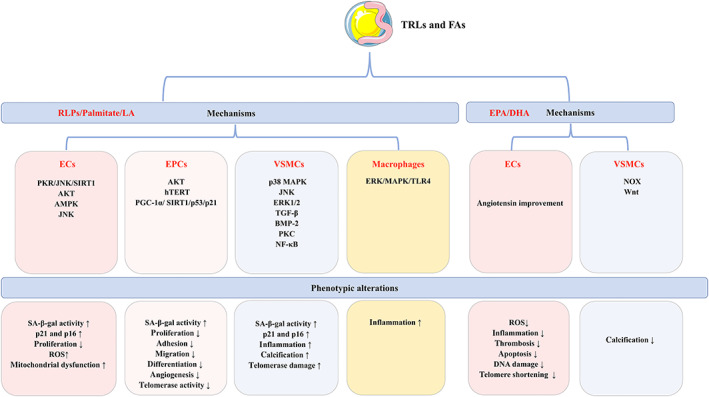
Cellular senescence of various types of cells induced by triglyceride‐rich lipoproteins (TRLs). TRLs and their hydrolysed products remnant‐like lipoproteins (RLPs) and fatty acids (FAs), influence various types of cellular senescence in atherosclerosis. RLPs, palmitate and linoleic acid (LA) promote senescence of these cells, while eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) exert anti‐senescence properties in atherosclerosis. AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate‐activated protein kinase; BMP‐2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; ECs, endothelial cells; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; ERK1/2, extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2; hTERT, human telomerase reverse transcriptase; JNK, c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; NF‐κB, nuclear factor kappa‐B; NOX, NADPH oxidase; PGC‐1α, peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor coactivator1‐α; PKC, protein kinase C; PKR, protein kinase R; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SA‐β‐gal, senescence‐associated β‐galactosidase; SIRT1, silent information regulator 1; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor β; TLR4, toll‐like receptor 4; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells; Wnt, wingless.
