FIGURE 1.
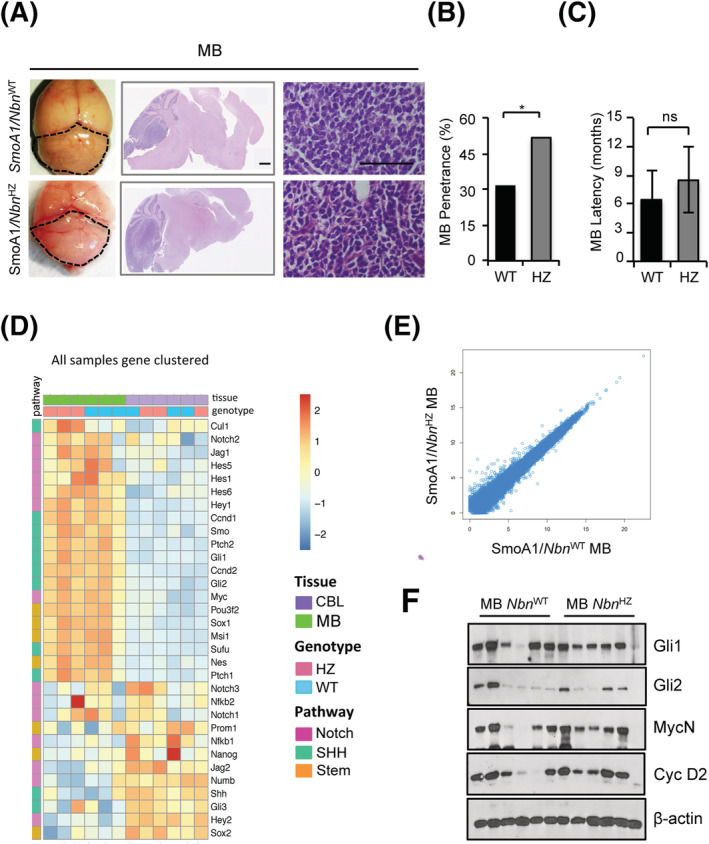
Monoallelic Nbn loss enhances Sonic Hedgehog (SHH)‐dependent medulloblastoma (MB) development. (A) Representative images of macroscopic features (left panels), haematoxylin/eosin‐stained sagittal sections (middle panels, scale bar: 1 mm) and high‐magnification view (right panels; scale bar 100 μM) of the brain/cerebella from adult mice with the indicated genotypes. Dotted lines highlight the size/shape of MB‐carrying cerebella. (B and C) Histograms representing MB penetrance (B) and latency (C) in SmoA1/Nbn WT and SmoA1/Nbn HZ mice. p‐Values were calculated by a one‐tailed chi‐square test (*p < 0.05) or two‐sided Student's t‐test (ns, not significant). (D) Heatmap of the RNA‐Seq data of the expression of the indicated transcripts in MB and healthy adult cerebella (CBL; 15 months) of SmoA1/Nbn WT (WT) and SmoA1/Nbn HZ (HZ) mice. The heatmap colour key denotes the gene expression value increasing from blue (low) to red (high). Gene expression values were clustered according to the column (samples) by exploiting a complete linkage hierarchical clustering algorithm and by using the Euclidean distance as distance metric. Pathway indication for each gene is also reported. (E) Scatter plot of the RNA‐Seq expression data in SmoA1/Nbn WT versus SmoA1/Nbn HZ tumours. Data are reported as the mean of the gene expression levels (in log‐scale) of three independent samples for each genetic background. (F) Western blot (WB) analysis of MB (n = 6) explanted from mice with the indicated genotypes
