Figure 3.
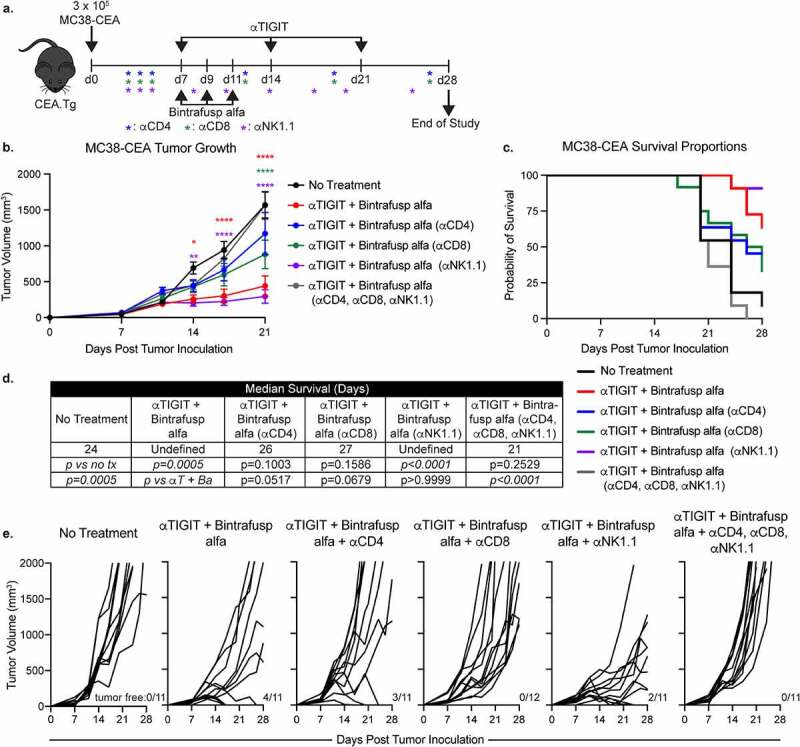
Antitumor activity and increase in overall survival from treatment with αTIGIT and bintrafusp alfa is dependent on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (a) Graphical representation of experimental design. (b) MC38-CEA tumor growth curves and (c) survival proportions of CEA.Tg animals treated with αTIGIT + bintrafusp alfa (red line; n = 11), αTIGIT + bintrafusp alfa depleted of CD4+ T cells (blue line; n = 11), αTIGIT + bintrafusp alfa depleted of CD8+ T cells (green line; n = 12), αTIGIT + bintrafusp alfa depleted of NK cells (purple line; n = 11), αTIGIT + bintrafusp alfa depleted of CD4+, CD8+ and NK cells (gray line; n = 11), and untreated animals (black line; n = 11). (d) Median survival of each treatment group. (e) Individual animal tumor growth rates of each treatment group. Numbers at the bottom right of tumor growth rate plots indicate tumor-free mice. * = p < .05, ** = p < .01, *** = p < .005, *** = p < .0001.
