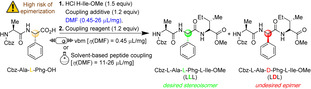
Table 7.
Comparative study between vibrating ball milling and solution synthesis of Z‐Ala‐Phg‐Ile‐OMe.[a,b] Adapted with permission from Ref. [115a]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
|
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Entry |
Reagents |
T [°C] |
t [min] |
Yield [%] |
Purity[b] [%] |
LDL[b] [%] |
|
1 |
EDC⋅HCl/ Oxyma |
33 (33) |
10 (30) |
93 (88) |
>99 (32) |
<1 (9) |
|
2 |
EDC⋅HCl/HOBt⋅H2O |
34 (34) |
10 (30) |
90 (90) |
70 (48) |
25 (35) |
|
3 |
EDC⋅HCl/HOAt |
34 (34) |
10 (30) |
88 (90) |
95 (59) |
<1 (26) |
|
4 |
DIC/HOAt |
30 (31) |
10 (40) |
n.d. (n.d.)[c] |
67 (39) |
17 (33) |
|
5 |
DIC/Oxyma |
31 (31) |
10 (40) |
n.d. (n.d.)[c] |
46 (<10) |
<1 (n.d.)[c] |
|
6 |
HATU/Et3N |
34 (34) |
10 (60) |
85 (88) |
88 (58) |
1 (<1) |
|
7 |
HBTU/Et3N |
33 (33) |
10 (20) |
86 (82) |
71 (55) |
2 (9) |
|
8 |
EDC⋅HCl/ Oxyma[d] |
n.d.[c] |
30 |
96 |
>99 |
<1 |
[a] Milling reactions were performed in a 5 mL polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) jar with three stainless‐steel balls (5 mm diameter) at 25 Hz. The total mass of reactants was 50 mg. The values in parentheses correspond to solution reactions. [b] LDL=undesired epimer; determined by HPLC. [c] n.d.=not determined. [d] Reaction was performed on a total mass of 250 mg of reactants in a 15 mL PTFE jar with one stainless‐steel ball (10 mm diameter) at 25 Hz for 30 min using 1.7 equiv. of EDC⋅HCl. EtOAc was used as a liquid additive instead of DMF.