Figure 6.
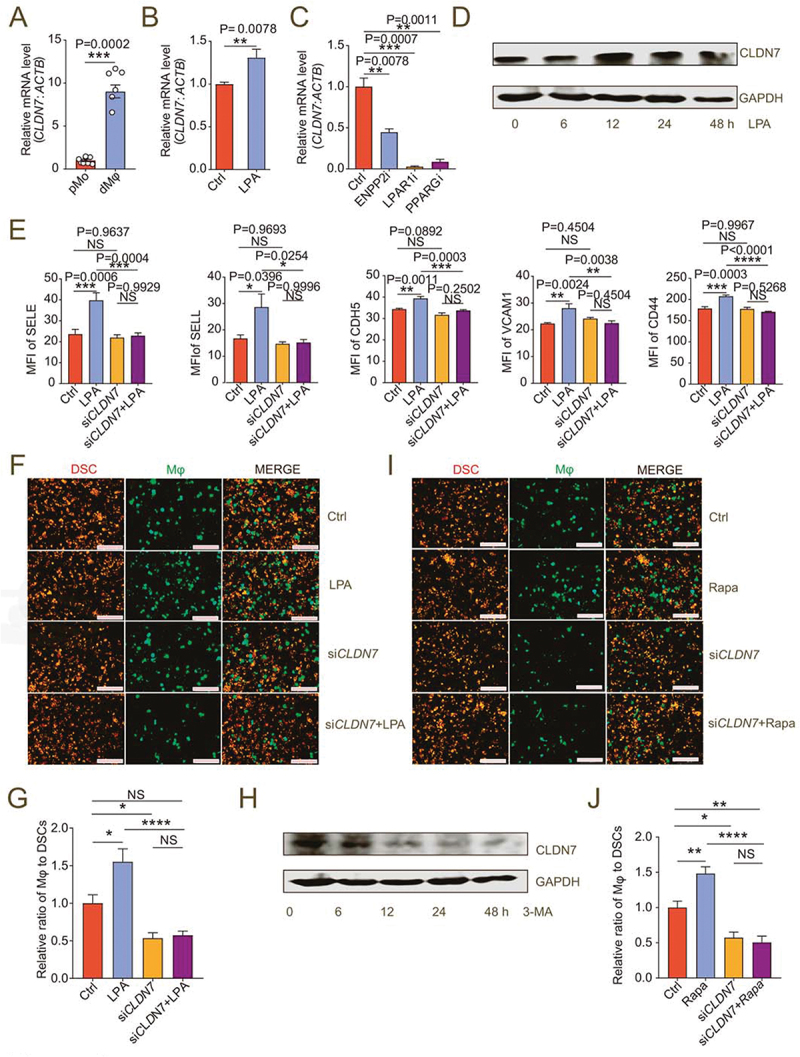
LPA/autophagy-mediated adhesion and residence of dMφ is dependent on CLDN7. (a) Transcription level of CLDN7 in pMo (n = 7) and dMφ (n = 6) by RT-PCR. (b) Transcription level of CLDN7 in control or LPA-treated (10 mM for 12 h) M0 macrophages by RT-PCR. (c) Transcription level of CLDN7 in control, ENPP2 inhibitor (100 nM), LPAR1 inhibitor (100 nM) or PPARG inhibitor (3.3 nM)-treated M2 macrophages by RT-PCR (12 h). (d) Western-blot for CLDN7 expression of M0 macrophages after treatment with LPA (10 μM) for 0, 6, 12, 24 or 48 h. (e) Flow cytometry assays for adhesion molecule expression of control, LPA-treated (10 μM for 24 h), CLDN7-silenced (siCLDN7) or LPA-treated (10 μM for 24 h) siCLDN7 macrophages. (f and g) Adhesion assays of control, LPA-treated (10 μM for 24 h), siCLDN7 or LPA-treated (10 μM for 24 h) siCLDN7 green-fluorescent dMφ to PKH-26-labeled red-fluorescent DSCs (n = 5). (h) Western-blot for levels of CLDN7 of M2 macrophage after treatment with 3-MA (10 mM) for 0, 6, 12, 24 or 48 h. (i and j) Adhesion assays of control, rapamycin-treated (2 μM for 24 h), siCLDN7 or rapamycin-treated (2 μM for 24 h) siCLDN7 green-fluorescent dMφ to red-fluorescent DSCs (n = 5). Data were presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by t test or one-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS: no significance.
