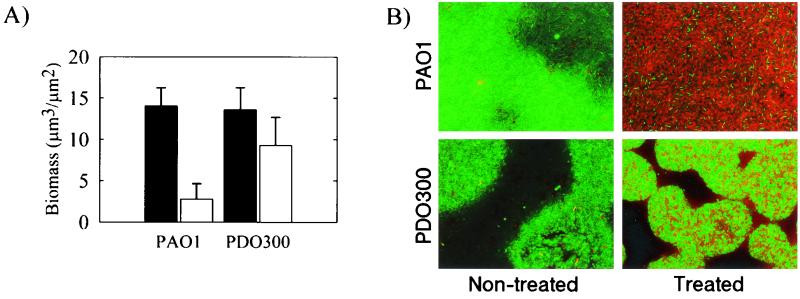
FIG. 4.
Increased tobramycin resistance of a P. aeruginosa PDO300 biofilm. (A) Viable biomass content of gfp-expressing P. aeruginosa wild-type and PDO300 mutant biofilms after 24 h of exposure to 2.0 μg of tobramycin per ml (open bars) and nontreated controls (filled bars). gfp fluorescence is a marker of cell viability and allows quantification of the viable biomass by COMSTAT image analysis of SCLM image data. (B) Visualization of live (green fluorescence) and dead (red fluorescence) cells by LIVE/DEAD BacLight bacterial viability staining kit. The treated biofilms were exposed to tobramycin as described above. Viability was measured by GFP fluorescence (A) and by SYTO 9 viability staining (B).