Figure 2.
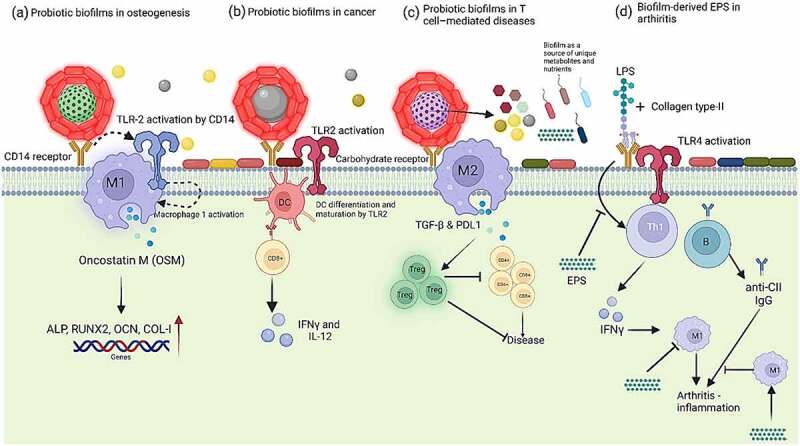
Probiotics in the form of biofilms are more effective than planktonic probiotic doses in several ways, especially in ameliorating diseases, as shown above in five different sections. (a) Polysaccharides on the surface of probiotic biofilms attach on CD14 of macrophages which leads to the activation of toll-like receptor cells (TLRs) signalling pathway. CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14) activates TLR2 to boost M1 macrophages phenotype which results in enhanced production of osteoinductive cytokines such as oncostatin M (OSM) to improve osteogenesis and it is evidenced by upregulation of osteogenic-related genes: runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), osteocalcin (OCN), and type I collagen (COL-I) 80 (b) Smectite laden with lactic acid bacteria biofilms inhibit tumor growth by activating dendritic cells (DCs) via Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) signalling (c) Exopolysaccharides from probiotic biofilms can induce M2 macrophages that inhibit CD4+ and CD8 + T cells by producing TGF-β and PD-L1 and possibly by induction of Tregs to prevent T-cell mediated diseases 81 (d) EPS from some LAB strain may inhibit T-cell proliferation and production of IFN-γ which leads to the polarization of M2 macrophage (an anti-inflammatory effect) and facilitates suppression of arthritogenic CII-specific IgG (T cell-dependent humoral response) – adapted from Nowak and colleagues.82 In addition, it has also been shown EPS from biofilms serve as a source of nutrients for commensals and probiotic biofilms also produce biofilm-specific metabolites which are not produced by planktonic doses.
