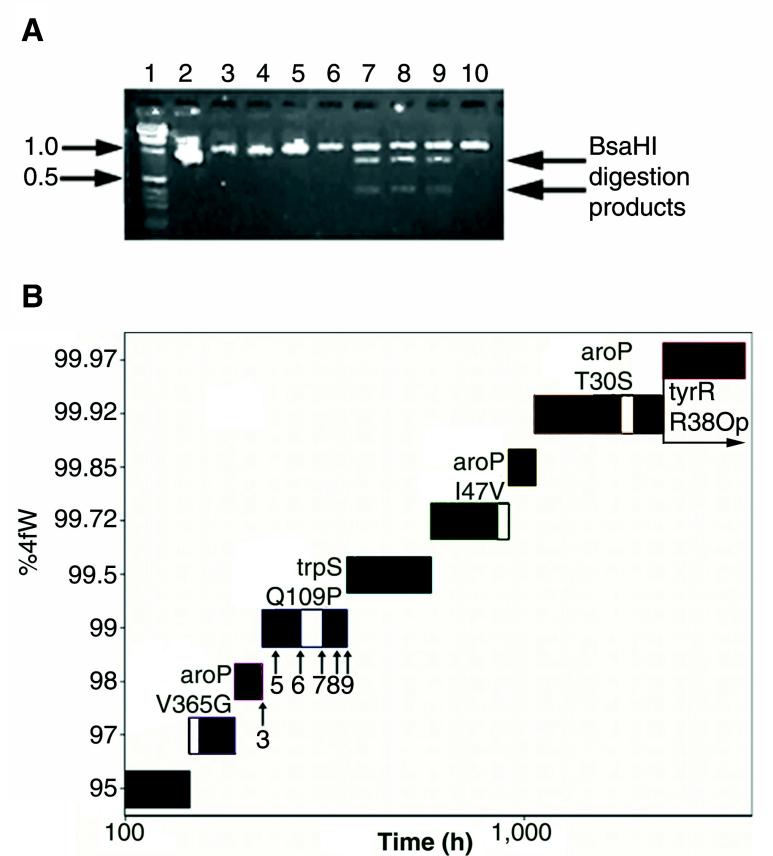
FIG. 7.
Serial introduction of functional mutations. (A) Evolutionary history of the trpS Q109P substitution. The Q109P substitution introduces a unique BsaHI site into the trpS gene. The trpS gene was amplified from different cultures and partially digested with BsaHI, and the fragments were separated on a 2% agarose gel. Lanes 1 and 2, 1-kb ladder and 1-kb standard; lanes 3 and 5 through 9, samples taken from the evolving strain, as indicated in Fig. 7B; lanes 4 and 10, samples taken from a parallel, unsuccessful strain, C600p-2, at time points identical to those shown in lanes 3 and 9, respectively. (B) Evolutionary history of the strain. The time spent at each ratio of 4fW to W is shown; time is on a log scale to simplify presentation. The white inserts represent the cultures in which individual mutations arose in either trpS or aroP. The timing of the sweep of the tyrR opal mutation could not be definitively located, beyond generalizing it to some time during the seven cultures grown at 99.97% 4fW. Arrows indicate the points at which samples were taken for trpS restriction analysis, and numbers refer to the gel lanes in Fig. 7A.