Figure 1.
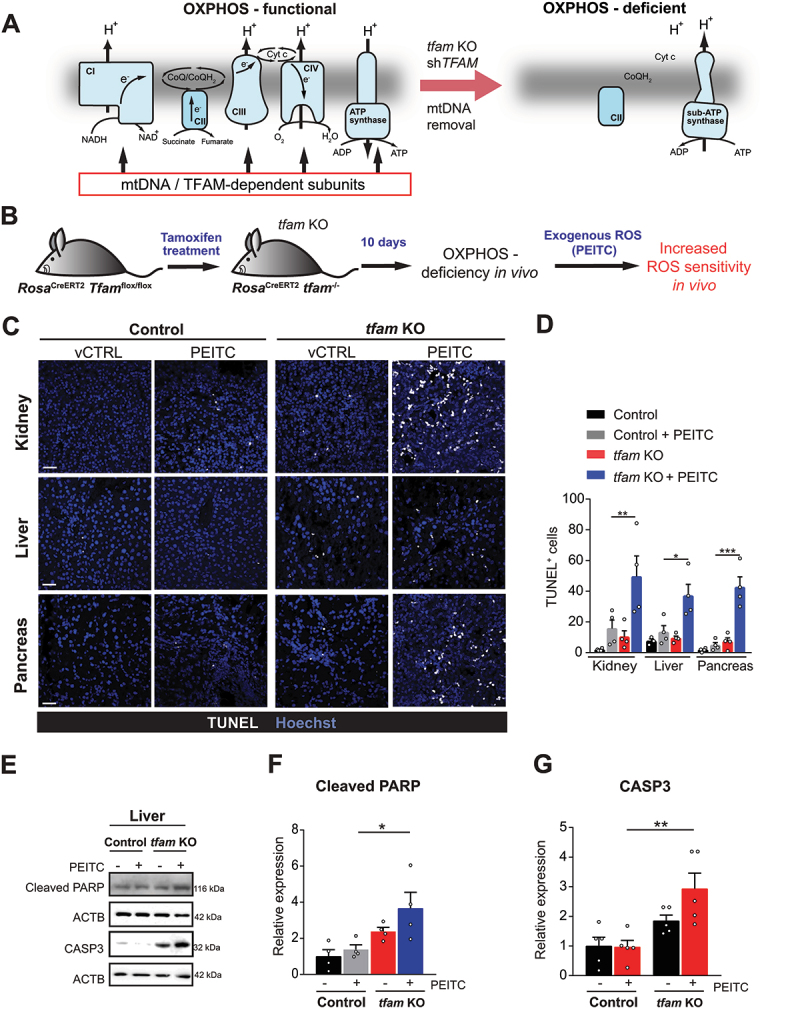
OXPHOS deficiency sensitizes to oxidative stress in vivo. (A) mtDNA removal, TFAM silencing or tfam deletion results in OXPHOS-deficient cells that lack ETC and contain a subcomplex of ATP synthase (sub-ATP synthase) that functions in reverse to hydrolyze ATP for ΔΨmi maintenance. (B) tfam deletion strategy in RosaCreERT2 Tfamflox/flox mice (referred to as tfam KO). (C) Representative images of cell death analyzed by TUNEL assay in kidney, liver and pancreas from vehicle-treated (vCTRL) and PEITC-treated control and tfam KO mice. Scale bar: 300 µm. (D) Quantification of TUNEL+ cells as shown in (C) (mean ± S.E.M., n = 4 mice per condition, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). (E) Representative WB images of the cleaved PARP and cleaved CASP3 in liver tissue of control and tfam KO mice treated or not with PEITC. (F and G) Densitometric quantification of WB in E and 3-4 additional independent experiments (normalized to ACTB, mean ± S.E.M., n ≥ 3 mice per condition, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test).
