Figure 6.
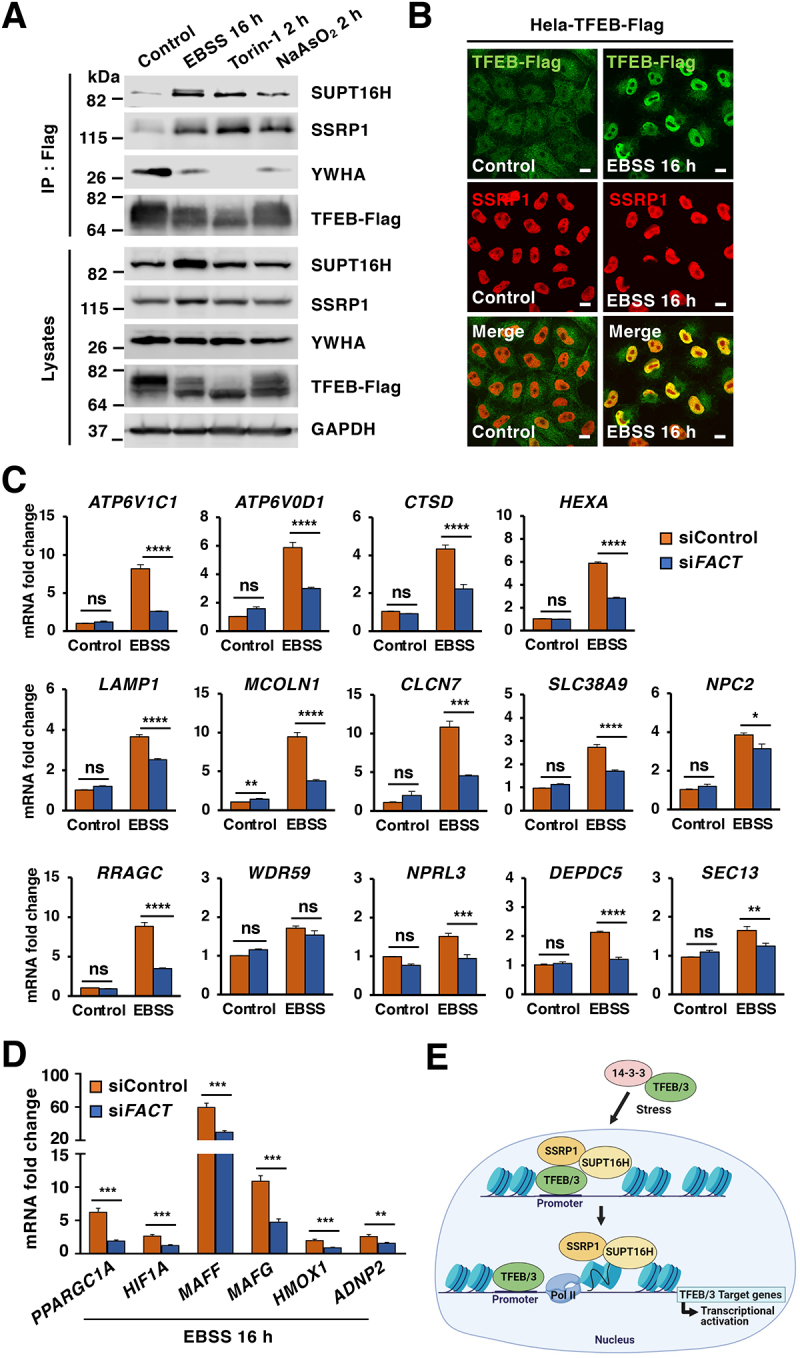
The FACT complex modulates TFEB transcriptional activity under starvation conditions. (A) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitated TFEB from HeLa-TFEB-Flag cells incubated with DMSO (Control), EBSS for 16 h, Torin-1 (250 nM) for 2 h or NaAsO2 (250 μM) for 2 h. (B) Immunofluorescence images of HeLa-TFEB-Flag cells treated with EBSS for 16 h and stained with antibodies against TFEB and SSRP1. Scale bars: 10 μm. (C) Relative quantitative real-time PCR analysis of ATP6V1C1, ATP6V0D1, CTSD, HEXA, LAMP1, MCOLN1, CLCN7, SLC38A9, NPC2, RRAGC, WDR59, NPRL3, DEPDC5, and SEC13 in control and FACT-depleted HeLa-TFEB-Flag cells upon incubation with EBSS for 16 h. Significance tested with two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001) from three independent experiments. (D) Relative quantitative real-time PCR analysis of PPARGC1A, HIF1A, MAFF, HMOX1, and ADNP2 mRNA transcript levels in control and FACT-depleted cells incubated with EBSS for 16 h compared to control condition. Data represented as geometric mean ± SD and significance tested with Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) from three independent experiments (E) Model depicting the proposed pathway of TFEB/TFE3-FACT complex activated by stress.
