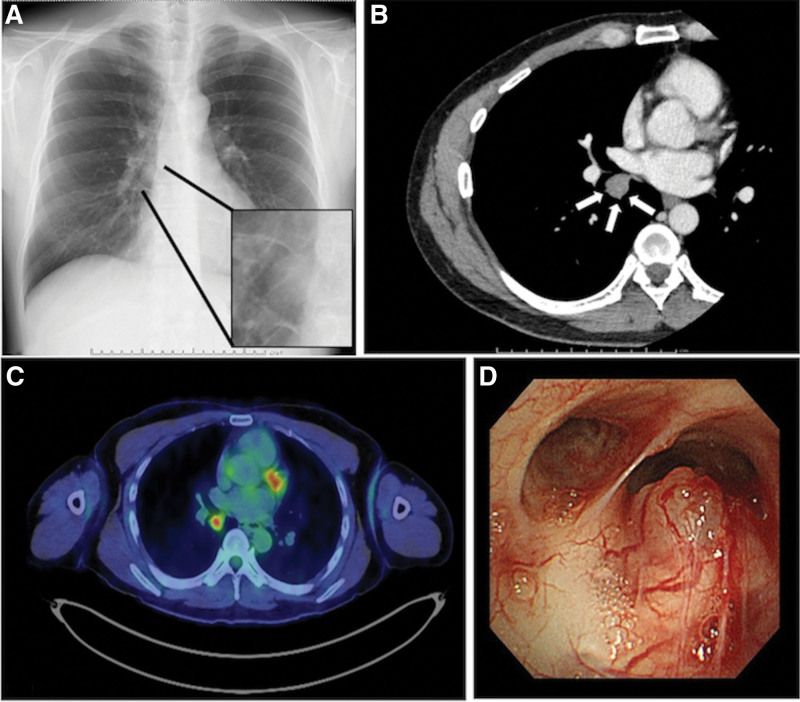
Figure 1.
(a) A nodule is noted on the chest radiograph (black arrows). (b) A 17-mm-sized nodule, with a mild contrast effect, is noted on contrast-enhanced CT (white arrows). (c) 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET-CT) reveals abnormal FDG accumulation in the nodule, with a maximum standardized uptake value of 4.07. (d) Bronchoscopy reveals a non-pulsating submucosal nodule, with proliferating capillary vessels, on the mucosal surface of the proximal end of the right intermediate bronchus.